Redis 管道
关键词:Pipeline
Pipeline 简介
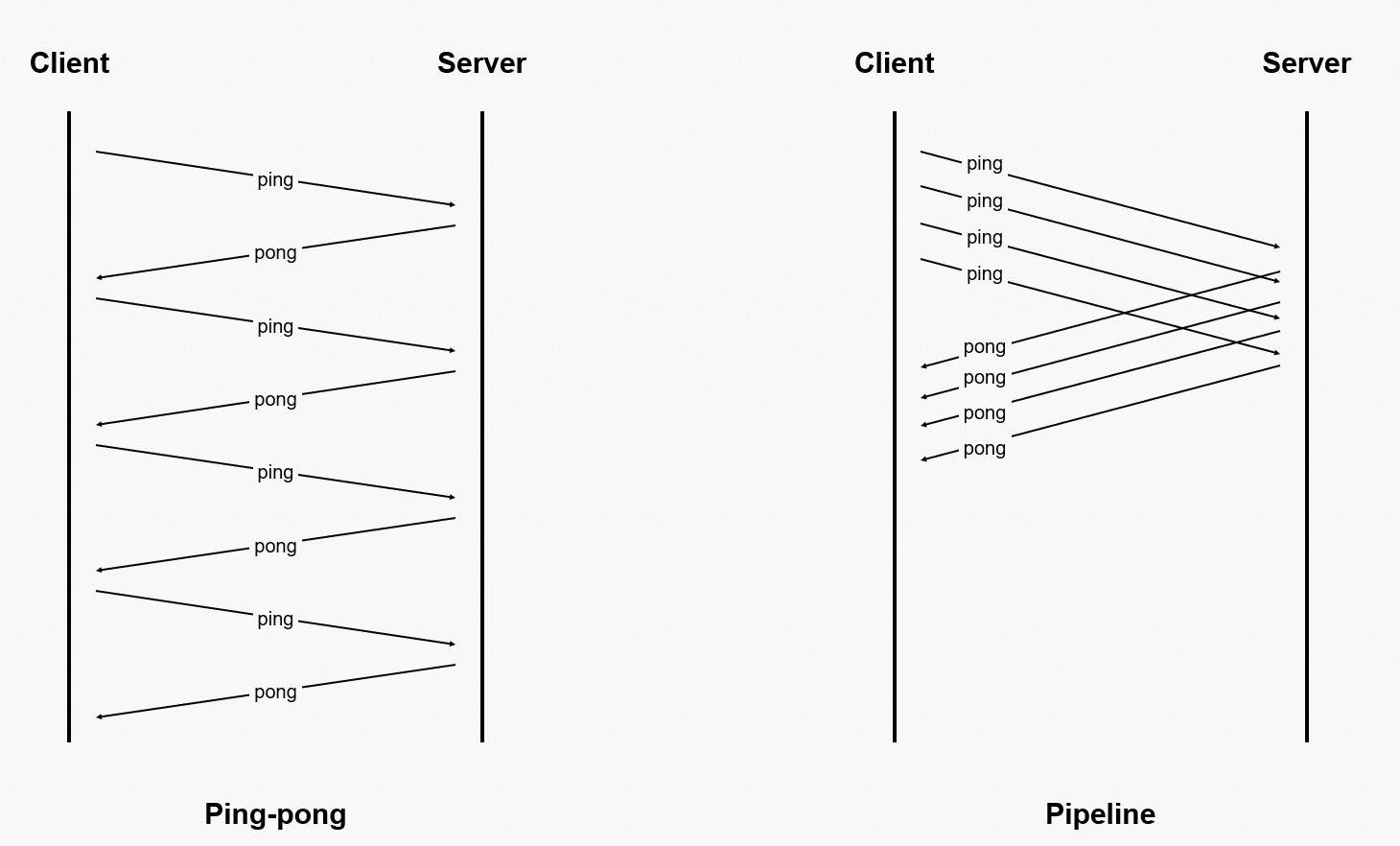
Redis 是一种基于 C/S 模型以及请求/响应协议的 TCP 服务。通常情况下,一个 Redis 命令的请求、响应遵循以下步骤:
- 客户端向服务端发送一个查询请求,并监听 Socket 返回(通常是以阻塞模式,等待服务端响应)。
- 服务端处理命令,并将结果返回给客户端。
显然,如果每个 Redis 命令都发起一次请求、响应,会很低效。因此,Redis 客户端提供了一种批量处理技术,即
管道技术(Pipeline)。Pipeline 的工作原理就是:将多个 Redis 命令一次性发送给服务端,服务端处理后,统一返回给客户端。由于减少了通信次数,自然提升了处理效率。
Pipeline 限制
在使用 Redis 管道技术时,要注意一些限制,避免踩坑:
- Pipeline 不能保证原子性 - Pipeline 只是将客户端发送命令的方式改为批量发送,而服务端在接收到 Pipeline 发来的命令后,将其拆解为一条条命令,然后依然是串行执行。执行过程中,服务端有可能执行其他客户端的命令,所以无法保证原子性。如需保证原子性,可以考虑使用事务或 Lua 脚本。
- Pipeline 不支持回滚 - Pipeline 没有事务的特性,如果待执行命令的前后存在依赖关系,请勿使用 Pipeline。
- Pipeline 命令不宜过大 - 使用管道发送命令时,Redis Server 会将部分请求放到缓存队列中(占用内存),执行完毕后一次性发送结果。如果需要发送大量的命令,会占用大量的内存,因此应该按照合理数量分批次的处理。
- Pipeline 不支持跨 slot 访问 - 由于 Pipeline 不支持跨 slot 访问,因此,在 Redis 集群模式下使用 Pipeline 时要确保访问的 key 都在同一 slot 中。
Pipeline 案例
主流的 Redis 客户端,一般都会支持管道技术。
【示例】Jedis 管道使用示例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
| public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String host = "localhost";
int port = 6379;
Jedis jedis = new Jedis(host, port);
String key = "pipeline:test";
jedis.del(key);
method1(jedis, key);
method2(jedis, key);
}
private static void method2(Jedis jedis, String key) {
System.out.println("-----方法2-----");
jedis.del(key);
Pipeline pipeline = jedis.pipelined();
Response<Long> r1 = pipeline.incr(key);
System.out.println("Pipeline发送请求");
Response<Long> r2 = pipeline.incr(key);
System.out.println("Pipeline发送请求");
Response<Long> r3 = pipeline.incr(key);
System.out.println("Pipeline发送请求");
Response<Long> r4 = pipeline.incr(key);
System.out.println("Pipeline发送请求");
Response<Long> r5 = pipeline.incr(key);
System.out.println("Pipeline发送请求");
try {
r1.get();
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println(" <<< Pipeline error:还未开始接收响应 >>> ");
}
System.out.println("发送请求完成,开始接收响应");
pipeline.sync();
System.out.println("Pipeline 接收响应 Response: " + r1.get());
System.out.println("Pipeline 接收响应 Response: " + r2.get());
System.out.println("Pipeline 接收响应 Response: " + r3.get());
System.out.println("Pipeline 接收响应 Response: " + r4.get());
System.out.println("Pipeline 接收响应 Response: " + r5.get());
jedis.close();
}
private static void method1(Jedis jedis, String key) {
Pipeline pipeline = jedis.pipelined();
System.out.println("-----方法1-----");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
pipeline.incr(key);
System.out.println("Pipeline 发送请求");
}
System.out.println("发送请求完成,开始接收响应");
List<Object> responses = pipeline.syncAndReturnAll();
if (responses == null || responses.isEmpty()) {
jedis.close();
throw new RuntimeException("Pipeline error: 没有接收到响应");
}
for (Object resp : responses) {
System.out.println("Pipeline 接收响应 Response: " + resp.toString());
}
System.out.println();
}
}
|
参考资料
