 JUnit5 快速入门
JUnit5 快速入门
# JUnit5 快速入门
# JUnit5 简介
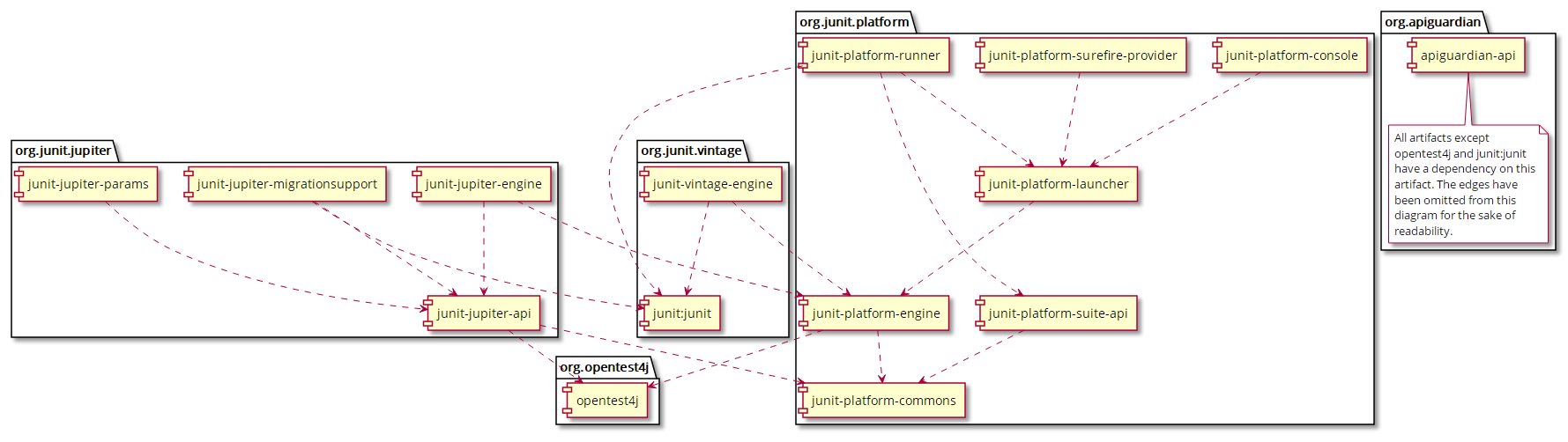
与以前的 JUnit 版本不同,JUnit 5 由来自三个不同子项目的几个不同模块组成。
JUnit 5 = JUnit Platform + JUnit Jupiter + JUnit Vintage
JUnit Platform 是在 JVM 上启动测试框架的基础。它还定义了用于开发在平台上运行的测试框架的 TestEngine API。此外,该平台还提供了一个控制台启动器,用于从命令行启动平台,并提供 JUnit 平台套件引擎,用于使用平台上的一个或多个测试引擎运行自定义测试套件。
JUnit Jupiter 是编程模型和扩展模型的组合,用于在 JUnit 5 中编写测试和扩展。Jupiter 子项目提供了一个 测试引擎(TestEngine )用于在平台上运行基于 Jupiter 的测试。
JUnit Vintage 提供了一个测试引擎(TestEngine ),用于在平台上运行基于 JUnit 3 和 JUnit 4 的测试。它要求 JUnit 4.12 或更高版本。
JUnit 5 在运行时需要 Java 8(或更高版本)。
# JUnit5 安装
在 pom 中添加依赖
<properties>
<junit.jupiter.version>5.3.2</junit.jupiter.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-params</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-engine</artifactId>
<version>${junit.jupiter.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
组件间依赖关系:
# JUnit5 注解
| Annotation | Description |
|---|---|
@Test | Denotes that a method is a test method. Unlike JUnit 4’s @Test annotation, this annotation does not declare any attributes, since test extensions in JUnit Jupiter operate based on their own dedicated annotations. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
@ParameterizedTest | Denotes that a method is a parameterized test (opens new window). Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
@RepeatedTest | Denotes that a method is a test template for a repeated test (opens new window). Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
@TestFactory | Denotes that a method is a test factory for dynamic tests (opens new window). Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
@TestInstance | Used to configure the test instance lifecycle (opens new window) for the annotated test class. Such annotations are inherited. |
@TestTemplate | Denotes that a method is a template for test cases (opens new window) designed to be invoked multiple times depending on the number of invocation contexts returned by the registered providers (opens new window). Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
@DisplayName | Declares a custom display name for the test class or test method. Such annotations are not inherited. |
@BeforeEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before each @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, or @TestFactory method in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @Before. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
@AfterEach | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after each @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, or @TestFactory method in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @After. Such methods are inherited unless they are overridden. |
@BeforeAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed before all @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, and @TestFactory methods in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @BeforeClass. Such methods are inherited (unless they are hidden or overridden) and must be static (unless the "per-class" test instance lifecycle (opens new window) is used). |
@AfterAll | Denotes that the annotated method should be executed after all @Test, @RepeatedTest, @ParameterizedTest, and @TestFactory methods in the current class; analogous to JUnit 4’s @AfterClass. Such methods are inherited (unless they are hidden or overridden) and must be static (unless the "per-class" test instance lifecycle (opens new window) is used). |
@Nested | Denotes that the annotated class is a nested, non-static test class. @BeforeAll and @AfterAllmethods cannot be used directly in a @Nested test class unless the "per-class" test instance lifecycle (opens new window) is used. Such annotations are not inherited. |
@Tag | Used to declare tags for filtering tests, either at the class or method level; analogous to test groups in TestNG or Categories in JUnit 4. Such annotations are inherited at the class level but not at the method level. |
@Disabled | Used to disable a test class or test method; analogous to JUnit 4’s @Ignore. Such annotations are not inherited. |
@ExtendWith | Used to register custom extensions (opens new window). Such annotations are inherited. |
# JUnit5 示例
我将一部分官方示例放在了我的个人项目中,可以直接下载测试。
示例源码路径:https://github.com/dunwu/java-tutorial/tree/master/codes/javatech/javatech-lib/src/test/java/io/github/dunwu/javatech/test/junit5
# 基本的单元测试类和方法
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
class Junit5StandardTests {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(Junit5StandardTests.class);
@BeforeAll
static void beforeAll() {
LOGGER.info("call beforeAll()");
}
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach() {
LOGGER.info("call beforeEach()");
}
@Test
void succeedingTest() {
LOGGER.info("call succeedingTest()");
}
@Test
void failingTest() {
LOGGER.info("call failingTest()");
// fail("a failing test");
}
@Test
@Disabled("for demonstration purposes")
void skippedTest() {
LOGGER.info("call skippedTest()");
// not executed
}
@AfterEach
void afterEach() {
LOGGER.info("call afterEach()");
}
@AfterAll
static void afterAll() {
LOGGER.info("call afterAll()");
}
}
# 定制测试类和方法的显示名称
支持普通字符、特殊符号、emoji
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@DisplayName("A special test case")
class JunitDisplayNameDemo {
@Test
@DisplayName("Custom test name containing spaces")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpaces() { }
@Test
@DisplayName("╯°□°)╯")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingSpecialCharacters() { }
@Test
@DisplayName("😱")
void testWithDisplayNameContainingEmoji() { }
}
# 断言(Assertions)
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeAll;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import static java.time.Duration.ofMillis;
import static java.time.Duration.ofMinutes;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.*;
class AssertionsDemo {
private static Person person;
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeAll() {
person = new Person("John", "Doe");
}
@Test
void standardAssertions() {
assertEquals(2, 2);
assertEquals(4, 4, "The optional assertion message is now the last parameter.");
assertTrue('a' < 'b', () -> "Assertion messages can be lazily evaluated -- "
+ "to avoid constructing complex messages unnecessarily.");
}
@Test
void groupedAssertions() {
// In a grouped assertion all assertions are executed, and any
// failures will be reported together.
assertAll("person", () -> assertEquals("John", person.getFirstName()),
() -> assertEquals("Doe", person.getLastName()));
}
@Test
void dependentAssertions() {
// Within a code block, if an assertion fails the
// subsequent code in the same block will be skipped.
assertAll("properties", () -> {
String firstName = person.getFirstName();
assertNotNull(firstName);
// Executed only if the previous assertion is valid.
assertAll("first name", () -> assertTrue(firstName.startsWith("J")),
() -> assertTrue(firstName.endsWith("n")));
}, () -> {
// Grouped assertion, so processed independently
// of results of first name assertions.
String lastName = person.getLastName();
assertNotNull(lastName);
// Executed only if the previous assertion is valid.
assertAll("last name", () -> assertTrue(lastName.startsWith("D")),
() -> assertTrue(lastName.endsWith("e")));
});
}
@Test
void exceptionTesting() {
Throwable exception = assertThrows(IllegalArgumentException.class, () -> {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("a message");
});
assertEquals("a message", exception.getMessage());
}
@Test
void timeoutNotExceeded() {
// The following assertion succeeds.
assertTimeout(ofMinutes(2), () -> {
// Perform task that takes less than 2 minutes.
});
}
@Test
void timeoutNotExceededWithResult() {
// The following assertion succeeds, and returns the supplied object.
String actualResult = assertTimeout(ofMinutes(2), () -> {
return "a result";
});
assertEquals("a result", actualResult);
}
@Test
void timeoutNotExceededWithMethod() {
// The following assertion invokes a method reference and returns an object.
String actualGreeting = assertTimeout(ofMinutes(2), AssertionsDemo::greeting);
assertEquals("Hello, World!", actualGreeting);
}
@Test
void timeoutExceeded() {
// The following assertion fails with an error message similar to:
// execution exceeded timeout of 10 ms by 91 ms
assertTimeout(ofMillis(10), () -> {
// Simulate task that takes more than 10 ms.
Thread.sleep(100);
});
}
@Test
void timeoutExceededWithPreemptiveTermination() {
// The following assertion fails with an error message similar to:
// execution timed out after 10 ms
assertTimeoutPreemptively(ofMillis(10), () -> {
// Simulate task that takes more than 10 ms.
Thread.sleep(100);
});
}
private static String greeting() {
return "Hello, World!";
}
}
# 假想(Assumptions)
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumeTrue;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assumptions.assumingThat;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class AssumptionsDemo {
@Test
void testOnlyOnCiServer() {
assumeTrue("CI".equals(System.getenv("ENV")));
// remainder of test
}
@Test
void testOnlyOnDeveloperWorkstation() {
assumeTrue("DEV".equals(System.getenv("ENV")),
() -> "Aborting test: not on developer workstation");
// remainder of test
}
@Test
void testInAllEnvironments() {
assumingThat("CI".equals(System.getenv("ENV")),
() -> {
// perform these assertions only on the CI server
assertEquals(2, 2);
});
// perform these assertions in all environments
assertEquals("a string", "a string");
}
}
# 禁用
禁用单元测试类示例:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@Disabled
class DisabledClassDemo {
@Test
void testWillBeSkipped() {
}
}
禁用单元测试方法示例:
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Disabled;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class DisabledTestsDemo {
@Disabled
@Test
void testWillBeSkipped() {
}
@Test
void testWillBeExecuted() {
}
}
# 测试条件
# 操作系统条件
@Test
@EnabledOnOs(MAC)
void onlyOnMacOs() {
// ...
}
@TestOnMac
void testOnMac() {
// ...
}
@Test
@EnabledOnOs({ LINUX, MAC })
void onLinuxOrMac() {
// ...
}
@Test
@DisabledOnOs(WINDOWS)
void notOnWindows() {
// ...
}
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Test
@EnabledOnOs(MAC)
@interface TestOnMac {
}
# Java 运行时版本条件
@Test
@EnabledOnJre(JAVA_8)
void onlyOnJava8() {
// ...
}
@Test
@EnabledOnJre({ JAVA_9, JAVA_10 })
void onJava9Or10() {
// ...
}
@Test
@DisabledOnJre(JAVA_9)
void notOnJava9() {
// ...
}
# 系统属性条件
@Test
@EnabledIfSystemProperty(named = "os.arch", matches = ".*64.*")
void onlyOn64BitArchitectures() {
// ...
}
@Test
@DisabledIfSystemProperty(named = "ci-server", matches = "true")
void notOnCiServer() {
// ...
}
# 嵌套测试
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertFalse;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertThrows;
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertTrue;
import java.util.EmptyStackException;
import java.util.Stack;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Nested;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
@DisplayName("A stack")
class TestingAStackDemo {
Stack<Object> stack;
@Test
@DisplayName("is instantiated with new Stack()")
void isInstantiatedWithNew() {
new Stack<>();
}
@Nested
@DisplayName("when new")
class WhenNew {
@BeforeEach
void createNewStack() {
stack = new Stack<>();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("is empty")
void isEmpty() {
assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when popped")
void throwsExceptionWhenPopped() {
assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, () -> stack.pop());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("throws EmptyStackException when peeked")
void throwsExceptionWhenPeeked() {
assertThrows(EmptyStackException.class, () -> stack.peek());
}
@Nested
@DisplayName("after pushing an element")
class AfterPushing {
String anElement = "an element";
@BeforeEach
void pushAnElement() {
stack.push(anElement);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("it is no longer empty")
void isNotEmpty() {
assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("returns the element when popped and is empty")
void returnElementWhenPopped() {
assertEquals(anElement, stack.pop());
assertTrue(stack.isEmpty());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("returns the element when peeked but remains not empty")
void returnElementWhenPeeked() {
assertEquals(anElement, stack.peek());
assertFalse(stack.isEmpty());
}
}
}
}
# 重复测试
import static org.junit.jupiter.api.Assertions.assertEquals;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.DisplayName;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepeatedTest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.RepetitionInfo;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.TestInfo;
class RepeatedTestsDemo {
private Logger logger = // ...
@BeforeEach
void beforeEach(TestInfo testInfo, RepetitionInfo repetitionInfo) {
int currentRepetition = repetitionInfo.getCurrentRepetition();
int totalRepetitions = repetitionInfo.getTotalRepetitions();
String methodName = testInfo.getTestMethod().get().getName();
logger.info(String.format("About to execute repetition %d of %d for %s", //
currentRepetition, totalRepetitions, methodName));
}
@RepeatedTest(10)
void repeatedTest() {
// ...
}
@RepeatedTest(5)
void repeatedTestWithRepetitionInfo(RepetitionInfo repetitionInfo) {
assertEquals(5, repetitionInfo.getTotalRepetitions());
}
@RepeatedTest(value = 1, name = "{displayName} {currentRepetition}/{totalRepetitions}")
@DisplayName("Repeat!")
void customDisplayName(TestInfo testInfo) {
assertEquals(testInfo.getDisplayName(), "Repeat! 1/1");
}
@RepeatedTest(value = 1, name = RepeatedTest.LONG_DISPLAY_NAME)
@DisplayName("Details...")
void customDisplayNameWithLongPattern(TestInfo testInfo) {
assertEquals(testInfo.getDisplayName(), "Details... :: repetition 1 of 1");
}
@RepeatedTest(value = 5, name = "Wiederholung {currentRepetition} von {totalRepetitions}")
void repeatedTestInGerman() {
// ...
}
}
# 参数化测试
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(strings = { "racecar", "radar", "able was I ere I saw elba" })
void palindromes(String candidate) {
assertTrue(isPalindrome(candidate));
}
# 参考资料
📝 帮助改善此页面! (opens new window)
上次更新: 2024/12/31, 08:02:35
