
- Java213
- 数据库114
- 分布式82
- 设计80
- 框架74
- JavaCore65
- Spring63
- 笔记52
- 工具50
- 大数据32
- 分布式通信29
- 设计模式28
- Spring核心24
- 架构23
- 搜索引擎数据库22
- DevOps21
- 关系型数据库21
- 软件20
- 网络19
- KV数据库19
- Redis18
- 算法17
- MQ17
- 分布式协同16
- Elasticsearch16
- 操作系统15
- 列式数据库15
- 分布式理论15
- MySQL15
- 综合14
- 面试13
- 基础特性13
- HBase13
- 编程12
- 文档数据库12
- Linux11
- IO11
- 并发11
- MongoDB11
- Spring数据10
- Kafka10
- 中间件9
- Flink9
- Hive9
- JVM9
- 其他9
- 安全9
- 构建9
- 工作8
- 服务器8
- 编程语言8
- 解决方案8
- 分布式存储8
- SpringWeb8
- 重构7
- 分布式调度7
- 容器7
- 高级特性7
- ZooKeeper7
- Maven7
- JavaWeb6
- 网络分层6
- 网络协议6
- 分布式治理6
- Tomcat6
- 监控诊断6
- Python6
- Nginx6
- Hadoop5
- 缓存5
- 测试5
- 微服务5
- Docker5
- Elastic5
- RPC5
- UML4
- 数据库综合4
- 网络技术4
- 术4
- 模板引擎4
- ORM4
- IDE4
- SpringIO4
- Spring其他4
- Spring综合4
- Spring集成4
- 软件工程3
- 编程范式3
- 数据库中间件3
- Git3
- Kubernetes3
- RocketMQ3
- 流量控制2
- JavaBean2
- 人工智能1
- 器1
- 法1
- KV 数据库1
- Spring安全1

概述
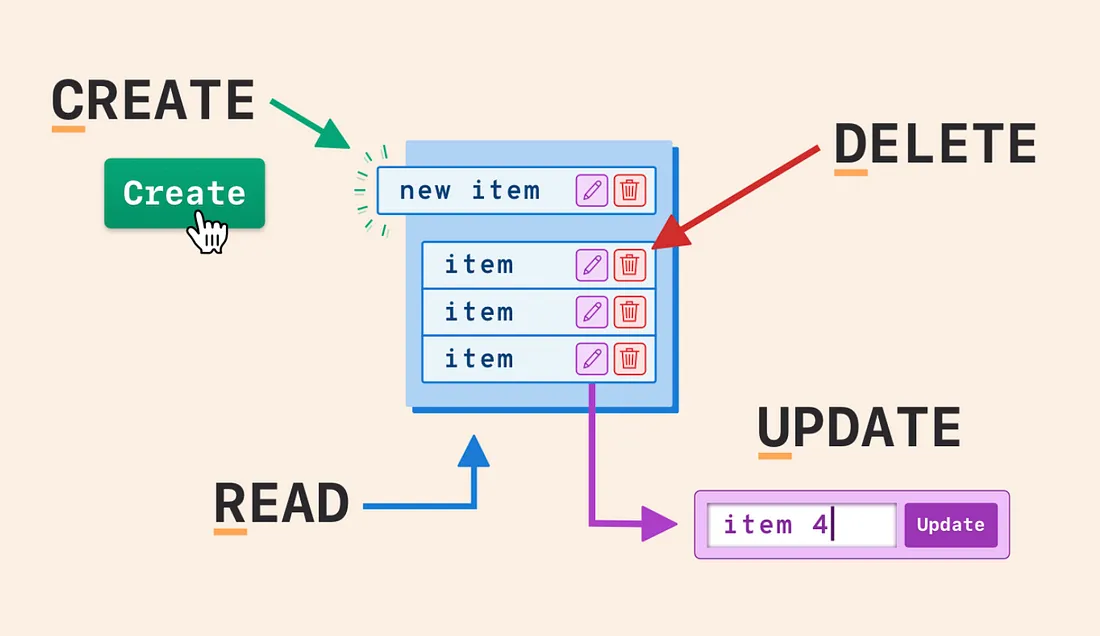
CRUD 由英文单词 Create, Read, Update, Delete 的首字母组成,即增删改查。
本文通过介绍基本的 MongoDB CRUD 方法,向读者呈现如何访问 MongoDB 数据。
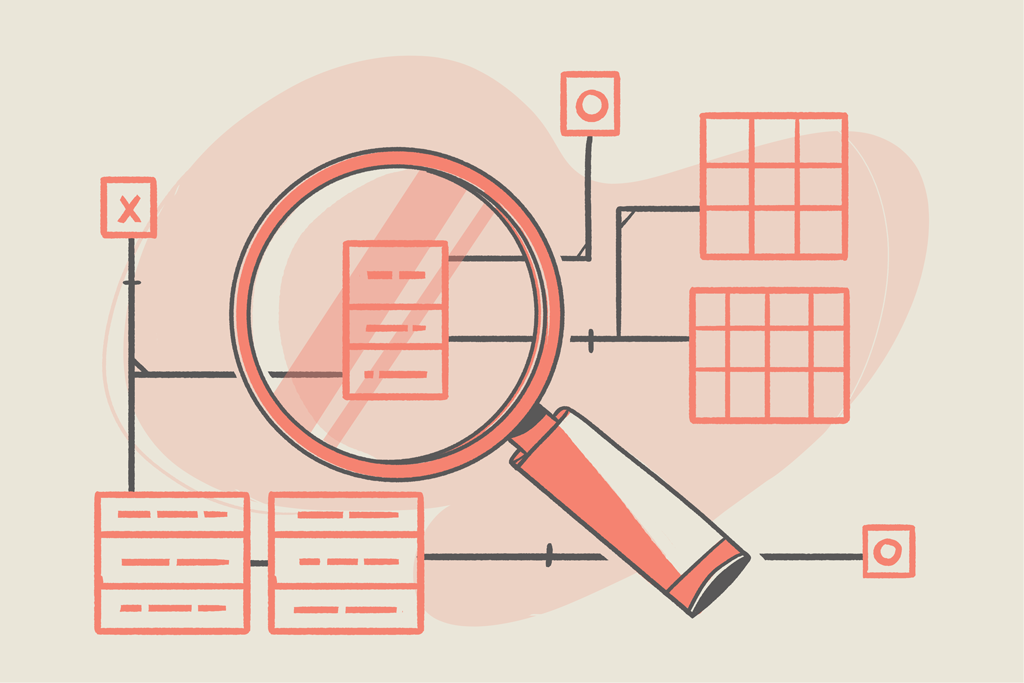

概述
索引通常能够极大的提高查询的效率。如果没有索引,MongoDB 在读取数据时必须扫描 collection 中的每个 document 并选取那些符合查询条件的记录。这种扫描全集合的查询是非常低效的,特别是在处理大量的数据时。查询可能要花费几十秒甚至几分钟,这种性能开销是不可接受的。索引可提高查询性能,但添加索引会影响写入操作的性能。对于写入读取率高的集合,由于每次插入操作都必须同时更新所有索引,因此会带来较高的索引成本。
本文介绍了 MongoDB 的基本索引操作、索引类型,和设置索引的策略。掌握了 MongoDB 索引的要点,有助于提高访问 MongoDB 数据的效率。
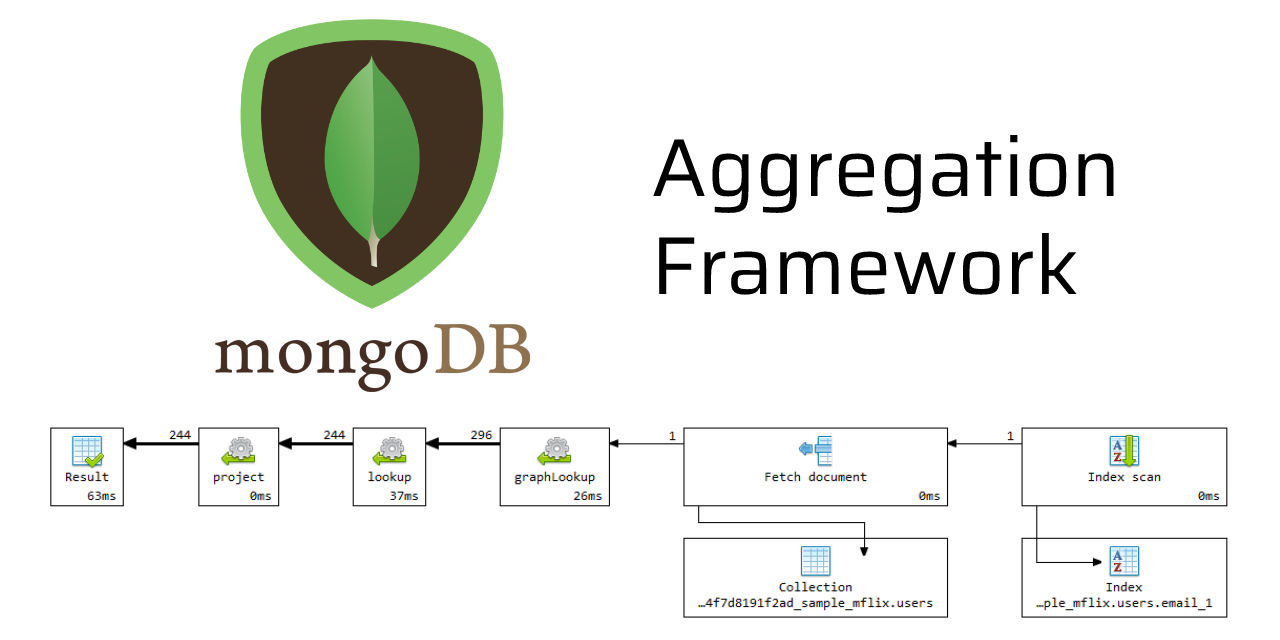
概述
聚合操作处理多个文档并返回计算结果。可以使用聚合操作来:
- 将多个文档中的值组合在一起。
- 对分组数据执行操作,返回单一结果。
- 分析一段时间内的数据变化。
在 MongoDB 中,支持以下聚合方式:
- 聚合管道,这是执行聚合的首选方法。
- 单一目的聚合方法,这些方法很简单,但缺乏聚合管道的功能。
- Map-Reduce,从 MongoDB 5.0 开始,Map-Reduce 已被弃用。聚合管道提供的性能和可用性比 Map-Reduce 更优越。
本文将逐一介绍这三种聚合方式的要点和使用方法。
概述
通俗的说,事务将多个读、写操作捆绑在一起成为一个逻辑操作单元。事务中的所有读写是一个执行的整体,整个事务要么成功(提交)、要么失败(中止或回滚)。如果失败,应用程序可以安全地重试。这样,由于不需要担心部分失败的情况(无论出于任何原因),应用层的错误处理就变得简单很多。
大多数 NoSQL 只能部分支持事务,甚至完全不支持事务。但是,MongoDB 支持 ACID 事务,这是它的一大优势。
本文主要介绍了 MongoDB 对于事务的支持力度,以及如何应用事务。
概述
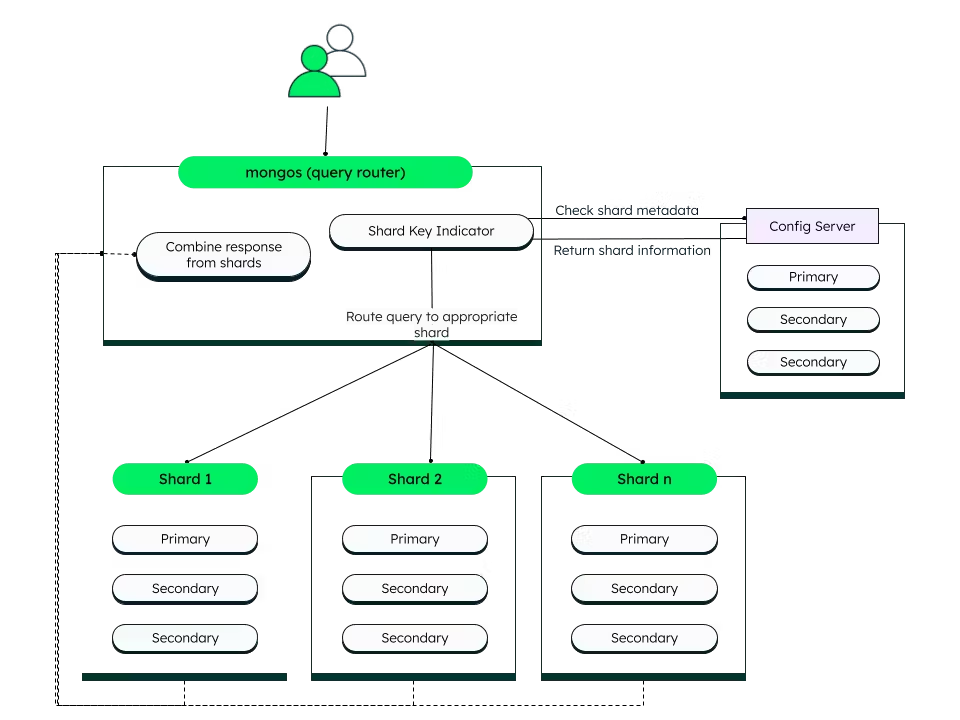
分区通常是这样定义的,即每一条数据(或者每条记录,每行或每个文档)只属于某个特定分区。实际上,每个分区都可以视为一个完整的小型数据库,虽然数据库可能存在一些跨分区的操作。
在不同系统中,分区有着不同的称呼,例如它对应于 MongoDB, Elasticsearch 和 SolrCloud 中的 shard, HBase 的 region, Bigtable 中的 tablet, Cassandra 和 Riak 中的 vnode ,以及 Couch base 中的 vBucket。
数据量如果太大,单台机器进行存储和处理就会成为瓶颈,因此需要引入数据分区机制。分区的目地是通过多台机器均匀分布数据和查询负载,避免出现热点。这需要选择合适的数据分区方案,在节点添加或删除时重新动态平衡分区。
分区通常与复制结合使用,即每个分区在多个节点都存有副本。这意味着某条记录属于特定的分区,而同样的内容会保存在不同的节点上以提高系统的容错性。一个节点上可能存储了多个分区。每个分区都有自己的主副本,例如被分配给某节点,而从副本则分配在其他一些节点。一个节点可能既是某些分区的主副本,同时又是其他分区的从副本。

概述
复制主要指通过网络在多台机器上保存相同数据的副本。
复制数据,可能出于各种各样的原因:
- 提高可用性 - 当部分组件出现位障,系统依然可以继续工作,系统依然可以继续工作。
- 降低访问延迟 - 使数据在地理位置上更接近用户。
- 提高读吞吐量 - 扩展至多台机器以同时提供数据访问服务。
综上可知,复制是所有分布式系统的核心特性,是高可用的重要保证。
MongoDB 本身是一个分布式数据库,自然也需要具备复制的能力。MongoDB 复制采用了经典的主从架构。所有的写入操作都发送到主节点,由主节点负责将数据更改事件发送到从节点,每个从节点都可以接收读请求。
本文将逐一阐述 MongoDB 复制的各个要点,以及如何基于复制来保证 MongoDB 的高可用。

概述
本文介绍了 MongoDB 的基本安装、备份和恢复、数据导入导出。
概述
MongoDB 是一个基于文档的分布式数据库,由 C++ 语言编写。旨在为 WEB 应用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案。
MongoDB 是一个介于关系型数据库和非关系型数据库之间的产品。它是非关系数据库当中功能最丰富,最像关系数据库的。它支持的数据结构非常松散,是类似 json 的 bson 格式,因此可以存储比较复杂的数据类型。
MongoDB 最大的特点是它支持的查询语言非常强大,其语法有点类似于面向对象的查询语言,几乎可以实现类似关系数据库单表查询的绝大部分功能,而且还支持对数据建立索引。