
ElasticSearch API
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式、RESTful 风格的搜索和数据分析引擎,能够解决不断涌现出的各种用例。 作为 Elastic Stack 的核心,它集中存储您的数据,帮助您发现意料之中以及意料之外的情况。
Elasticsearch 基于搜索库 Lucene 开发。ElasticSearch 隐藏了 Lucene 的复杂性,提供了简单易用的 REST API / Java API 接口(另外还有其他语言的 API 接口)。
以下简称 ES。
REST API 最详尽的文档应该参考:ES 官方 REST API
ElasticSearch API 简介
Elasticsearch 官方提供了很多版本的 Java 客户端,包含但不限于:
- Transport Client - 7.0 废弃,8.0 移除。
- Java REST 客户端
- Elasticsearch Java API Client -
如果当前是:8.X 版本,推荐 Elasticsearch Java API客户端。
如果当前是:7.X 版本且不考虑升级,推荐 High Level REST客户端。
如果当前是:5.X、6.X 版本,推荐尽早升级集群版本。
Elasticsearch Java API Client 快速入门
:::detail 示例
//创建一个低级的客户端
final RestClient restClient = RestClient.builder(new HttpHost("localhost", 9200)).build();
//创建 JSON 对象映射器
final RestClientTransport transport = new RestClientTransport(restClient, new JacksonJsonpMapper());
//创建 API 客户端
final ElasticsearchClient client = new ElasticsearchClient(transport);
//查询所有索引-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
final GetIndexResponse response = client.indices().get(query -> query.index("_all"));
final IndexState products = response.result().get("products");
System.out.println(products.toString());
//关闭
client.shutdown();
transport.close();
restClient.close();
:::
Transport Client 快速入门
TransportClient 使用 transport 模块远程连接到 Elasticsearch 集群。它不会加入集群,而只是获取一个或多个初始传输地址,并以轮询方式与它们通信。
扩展:https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/client/java-api/current/transport-client.html
:::detail 示例
启动客户端:
// 启动
TransportClient client = new PreBuiltTransportClient(Settings.EMPTY)
.addTransportAddress(new TransportAddress(InetAddress.getByName("host1"), 9300))
.addTransportAddress(new TransportAddress(InetAddress.getByName("host2"), 9300));
// 关闭
client.close();
配置集群名称
注意,如果使用的集群名称与 “elasticsearch” 不同,则必须设置集群名称。
Settings settings = Settings.builder()
.put("cluster.name", "myClusterName").build();
TransportClient client = new PreBuiltTransportClient(settings);
// Add transport addresses and do something with the client...
启用 sniffing
Settings settings = Settings.builder()
.put("client.transport.sniff", true).build();
TransportClient client = new PreBuiltTransportClient(settings);
:::
ElasticSearch Rest
ElasticSearch Rest API 语法格式
向 Elasticsearch 发出的请求的组成部分与其它普通的 HTTP 请求是一样的:
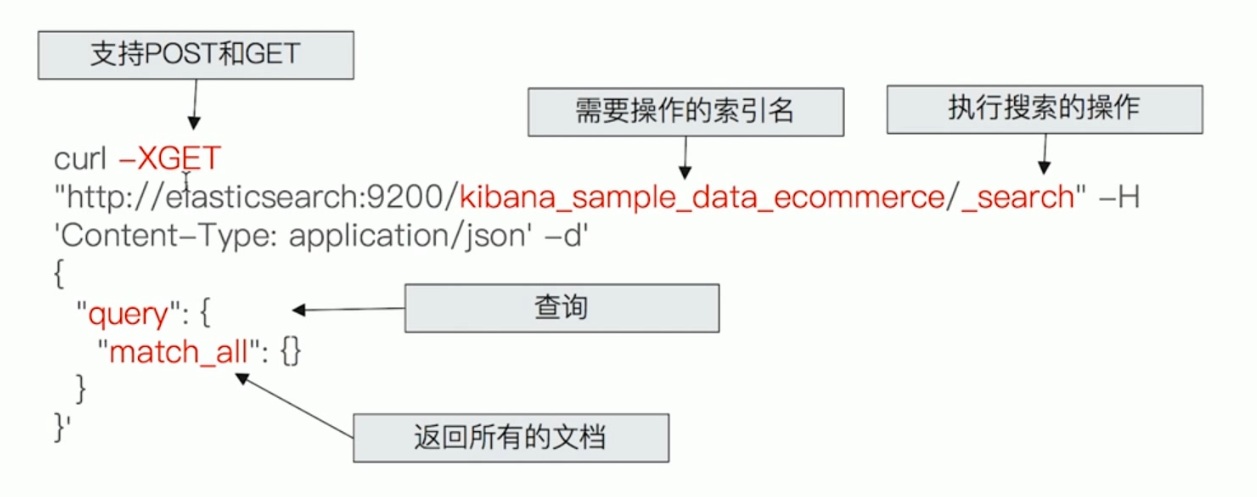
curl -X<VERB> '<PROTOCOL>://<HOST>:<PORT>/<PATH>?<QUERY_STRING>' -d '<BODY>'
VERB:HTTP 方法,支持:GET,POST,PUT,HEAD,DELETEPROTOCOL:http 或者 https 协议(只有在 Elasticsearch 前面有 https 代理的时候可用)HOST:Elasticsearch 集群中的任何一个节点的主机名,如果是在本地的节点,那么就叫 localhostPORT:Elasticsearch HTTP 服务所在的端口,默认为 9200 PATH API 路径(例如、_count 将返回集群中文档的数量),PATH:可以包含多个组件,例如_cluster/stats或者_nodes/stats/jvmQUERY_STRING:一些可选的查询请求参数,例如?pretty 参数将使请求返回更加美观易读的 JSON 数据BODY:一个 JSON 格式的请求主体(如果请求需要的话)
ElasticSearch Rest API 分为两种:
- URI Search:在 URL 中使用查询参数
- Request Body Search:基于 JSON 格式的、更加完备的 DSL
URI Search 示例:

Request Body Search 示例:
索引 API
创建索引
新建 Index,可以直接向 ES 服务器发出 PUT 请求。
语法格式:
PUT /my_index
{
"settings": { ... any settings ... },
"mappings": {
"type_one": { ... any mappings ... },
"type_two": { ... any mappings ... },
...
}
}
示例:
PUT /user
{
"settings": {
"index": {
"number_of_shards": 3,
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
}
}
服务器返回一个 JSON 对象,里面的 acknowledged 字段表示操作成功。
{"acknowledged":true,"shards_acknowledged":true,"index":"user"}
如果你想禁止自动创建索引,可以通过在 config/elasticsearch.yml 的每个节点下添加下面的配置:
action.auto_create_index: false
删除索引
然后,我们可以通过发送 DELETE 请求,删除这个 Index。
DELETE /user
删除多个索引
DELETE /index_one,index_two
DELETE /index_*
查看索引
可以通过 GET 请求查看索引信息
# 查看索引相关信息
GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
# 查看索引的文档总数
GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_count
# 查看前 10 条文档,了解文档格式
GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
# _cat indices API
# 查看 indices
GET /_cat/indices/kibana*?v&s=index
# 查看状态为绿的索引
GET /_cat/indices?v&health=green
# 按照文档个数排序
GET /_cat/indices?v&s=docs.count:desc
# 查看具体的字段
GET /_cat/indices/kibana*?pri&v&h=health,index,pri,rep,docs.count,mt
# 查看索引占用的内存
GET /_cat/indices?v&h=i,tm&s=tm:desc
索引别名
ES 的索引别名就是给一个索引或者多个索引起的另一个名字,典型的应用场景是针对索引使用的平滑切换。
首先,创建索引 my_index,然后将别名 my_alias 指向它,示例如下:
PUT /my_index
PUT /my_index/_alias/my_alias
也可以通过如下形式:
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{ "add": { "index": "my_index", "alias": "my_alias" }}
]
}
也可以在一次请求中增加别名和移除别名混合使用:
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{ "remove": { "index": "my_index", "alias": "my_alias" }}
{ "add": { "index": "my_index_v2", "alias": "my_alias" }}
]
}
需要注意的是,如果别名与索引是一对一的,使用别名索引文档或者查询文档是可以的,但是如果别名和索引是一对多的,使用别名会发生错误,因为 ES 不知道把文档写入哪个索引中去或者从哪个索引中读取文档。
ES 索引别名有个典型的应用场景是平滑切换,更多细节可以查看 Elasticsearch(ES)索引零停机(无需重启)无缝平滑切换的方法。
打开/关闭索引
通过在 POST 中添加 _close 或 _open 可以打开、关闭索引。
打开索引
# 打开索引
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_open
# 关闭索引
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_close
文档
############Create Document############
#create document. 自动生成 _id
POST users/_doc
{
"user" : "Mike",
"post_date" : "2019-04-15T14:12:12",
"message" : "trying out Kibana"
}
#create document. 指定 Id。如果 id 已经存在,报错
PUT users/_doc/1?op_type=create
{
"user" : "Jack",
"post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12",
"message" : "trying out Elasticsearch"
}
#create document. 指定 ID 如果已经存在,就报错
PUT users/_create/1
{
"user" : "Jack",
"post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12",
"message" : "trying out Elasticsearch"
}
### Get Document by ID
#Get the document by ID
GET users/_doc/1
### Index & Update
#Update 指定 ID (先删除,在写入)
GET users/_doc/1
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"user" : "Mike"
}
#GET users/_doc/1
#在原文档上增加字段
POST users/_update/1/
{
"doc":{
"post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12",
"message" : "trying out Elasticsearch"
}
}
### Delete by Id
# 删除文档
DELETE users/_doc/1
### Bulk 操作
#执行两次,查看每次的结果
#执行第 1 次
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "field1" : "value1" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test2", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "field1" : "value3" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_index" : "test"} }
{ "doc" : {"field2" : "value2"} }
#执行第 2 次
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "field1" : "value1" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test2", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "field1" : "value3" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_index" : "test"} }
{ "doc" : {"field2" : "value2"} }
### mget 操作
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "1"
},
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "2"
}
]
}
#URI 中指定 index
GET /test/_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_id" : "1"
},
{
"_id" : "2"
}
]
}
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_source" : false
},
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "2",
"_source" : ["field3", "field4"]
},
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "3",
"_source" : {
"include": ["user"],
"exclude": ["user.location"]
}
}
]
}
### msearch 操作
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_msearch
{}
{"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size":1}
{"index" : "kibana_sample_data_flights"}
{"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size":2}
### 清除测试数据
#清除数据
DELETE users
DELETE test
DELETE test2
创建文档
指定 ID
语法格式:
PUT /_index/_type/_create/_id
示例:
PUT /user/_doc/_create/1
{
"user": "张三",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "数据库管理"
}
注意:指定 Id,如果 id 已经存在,则报错
自动生成 ID
新增记录的时候,也可以不指定 Id,这时要改成 POST 请求。
语法格式:
POST /_index/_type
示例:
POST /user/_doc
{
"user": "张三",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "超级管理员"
}
删除文档
语法格式:
DELETE /_index/_doc/_id
示例:
DELETE /user/_doc/1
更新文档
先删除,再写入
语法格式:
PUT /_index/_type/_id
示例:
PUT /user/_doc/1
{
"user": "李四",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "超级管理员"
}
在原文档上增加字段
语法格式:
POST /_index/_update/_id
示例:
POST /user/_update/1
{
"doc":{
"age" : "30"
}
}
查询文档
指定 ID 查询
语法格式:
GET /_index/_type/_id
示例:
GET /user/_doc/1
结果:
{
"_index": "user",
"_type": "_doc",
"_id": "1",
"_version": 1,
"_seq_no": 536248,
"_primary_term": 2,
"found": true,
"_source": {
"user": "张三",
"title": "工程师",
"desc": "数据库管理"
}
}
返回的数据中,found 字段表示查询成功,_source 字段返回原始记录。
如果 id 不正确,就查不到数据,found 字段就是 false
查询所有记录
使用 GET 方法,直接请求 /index/type/_search,就会返回所有记录。
$ curl 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search?pretty'
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 3,
"successful" : 3,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "admin",
"_id" : "WWuoDG8BHwECs7SiYn93",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"user" : "李四",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "系统管理"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "admin",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"user" : "张三",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "超级管理员"
}
}
]
}
}
上面代码中,返回结果的 took字段表示该操作的耗时(单位为毫秒),timed_out字段表示是否超时,hits字段表示命中的记录,里面子字段的含义如下。
total:返回记录数,本例是 2 条。max_score:最高的匹配程度,本例是1.0。hits:返回的记录组成的数组。
返回的记录中,每条记录都有一个_score字段,表示匹配的程序,默认是按照这个字段降序排列。
全文搜索
ES 的查询非常特别,使用自己的 查询语法,要求 GET 请求带有数据体。
$ curl -H 'Content-Type: application/json' 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "管理" }}
}'
上面代码使用 Match 查询,指定的匹配条件是desc字段里面包含"软件"这个词。返回结果如下。
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 3,
"successful" : 3,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : 2,
"max_score" : 0.38200712,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "admin",
"_id" : "WWuoDG8BHwECs7SiYn93",
"_score" : 0.38200712,
"_source" : {
"user" : "李四",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "系统管理"
}
},
{
"_index" : "user",
"_type" : "admin",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.3487891,
"_source" : {
"user" : "张三",
"title" : "工程师",
"desc" : "超级管理员"
}
}
]
}
}
Elastic 默认一次返回 10 条结果,可以通过size字段改变这个设置,还可以通过from字段,指定位移。
$ curl 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "管理" }},
"from": 1,
"size": 1
}'
上面代码指定,从位置 1 开始(默认是从位置 0 开始),只返回一条结果。
逻辑运算
如果有多个搜索关键字, Elastic 认为它们是or关系。
$ curl 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search' -d '
{
"query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "软件 系统" }}
}'
上面代码搜索的是软件 or 系统。
如果要执行多个关键词的and搜索,必须使用 布尔查询。
$ curl -H 'Content-Type: application/json' 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search?pretty' -d '
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "desc": "管理" } },
{ "match": { "desc": "超级" } }
]
}
}
}'
批量执行
支持在一次 API 调用中,对不同的索引进行操作
支持四种类型操作
- index
- create
- update
- delete
操作中单条操作失败,并不会影响其他操作。
返回结果包括了每一条操作执行的结果。
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "field1" : "value1" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test2", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "field1" : "value3" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_index" : "test"} }
{ "doc" : {"field2" : "value2"} }
说明:上面的示例如果执行多次,执行结果都不一样。
批量读取
读多个索引
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "1"
},
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "2"
}
]
}
读一个索引
GET /test/_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_id" : "1"
},
{
"_id" : "2"
}
]
}
GET /_mget
{
"docs" : [
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "1",
"_source" : false
},
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "2",
"_source" : ["field3", "field4"]
},
{
"_index" : "test",
"_id" : "3",
"_source" : {
"include": ["user"],
"exclude": ["user.location"]
}
}
]
}
批量查询
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_msearch
{}
{"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size":1}
{"index" : "kibana_sample_data_flights"}
{"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size":2}
URI Search 查询语义
Elasticsearch URI Search 遵循 QueryString 查询语义,其形式如下:
GET /movies/_search?q=2012&df=title&sort=year:desc&from=0&size=10&timeout=1s
{
"profile": true
}
q指定查询语句,使用 QueryString 语义df默认字段,不指定时sort排序:from 和 size 用于分页profile可以查看查询时如何被执行的
GET /movies/_search?q=title:2012&sort=year:desc&from=0&size=10&timeout=1s
{
"profile":"true"
}
Term 和 Phrase
Beautiful Mind 等效于 Beautiful OR Mind
"Beautiful Mind" 等效于 Beautiful AND Mind
# Term 查询
GET /movies/_search?q=title:Beautiful Mind
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 使用引号,Phrase 查询
GET /movies/_search?q=title:"Beautiful Mind"
{
"profile":"true"
}
分组与引号
title:(Beautiful AND Mind)
title="Beautiful Mind"
AND、OR、NOT 或者 &&、||、!
注意:AND、OR、NOT 必须大写
# 布尔操作符
GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful AND Mind)
{
"profile":"true"
}
GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful NOT Mind)
{
"profile":"true"
}
范围查询
[]表示闭区间{}表示开区间
示例:
# 范围查询 , 区间写法
GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautiful AND year:{2010 TO 2018%7D
{
"profile":"true"
}
GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautiful AND year:[* TO 2018]
{
"profile":"true"
}
算数符号
# 2010 年以后的记录
GET /movies/_search?q=year:>2010
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 2010 年到 2018 年的记录
GET /movies/_search?q=year:(>2010 && <=2018)
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 2010 年到 2018 年的记录
GET /movies/_search?q=year:(+>2010 +<=2018)
{
"profile":"true"
}
通配符查询
?代表 1 个字符*代表 0 或多个字符
示例:
GET /movies/_search?q=title:mi?d
{
"profile":"true"
}
GET /movies/_search?q=title:b*
{
"profile":"true"
}
正则表达式
title:[bt]oy
模糊匹配与近似查询
示例:
# 相似度在 1 个字符以内
GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautifl~1
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 相似度在 2 个字符以内
GET /movies/_search?q=title:"Lord Rings"~2
{
"profile":"true"
}
Request Body & DSL
Elasticsearch 除了 URI Search 查询方式,还支持将查询语句通过 Http Request Body 发起查询。
GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true
{
"profile":"true",
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
分页
GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true
{
"profile": "true",
"from": 0,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
排序
最好在数字型或日期型字段上排序
因为对于多值类型或分析过的字段排序,系统会选一个值,无法得知该值
GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true
{
"profile": "true",
"sort": [
{
"order_date": "desc"
}
],
"from": 1,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
_source 过滤
如果 _source 没有存储,那就只返回匹配的文档的元数据
_source 支持使用通配符,如:_source["name*", "desc*"]
示例:
GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true
{
"profile": "true",
"_source": [
"order_date",
"category.keyword"
],
"from": 1,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
脚本字段
GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true
{
"profile": "true",
"script_fields": {
"new_field": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source":"doc['order_date'].value+' hello'"
}
}
},
"from": 1,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
使用查询表达式 - Match
POST movies/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "last christmas"
}
}
}
POST movies/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "last christmas",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
短语搜索 - Match Phrase
POST movies/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title":{
"query": "last christmas"
}
}
}
}
集群 API
一些集群级别的 API 可能会在节点的子集上运行,这些节点可以用节点过滤器指定。例如,任务管理、节点统计和节点信息 API 都可以报告来自一组过滤节点而不是所有节点的结果。
节点过滤器以逗号分隔的单个过滤器列表的形式编写,每个过滤器从所选子集中添加或删除节点。每个过滤器可以是以下之一:
_all:将所有节点添加到子集_local:将本地节点添加到子集_master:将当前主节点添加到子集- 根据节点 ID 或节点名将匹配节点添加到子集
- 根据 IP 地址或主机名将匹配节点添加到子集
- 使用通配符,将节点名、地址名或主机名匹配的节点添加到子集
master:true,data:true,ingest:true,voting_only:true,ml:true或coordinating_only:true, 分别意味着将所有主节点、所有数据节点、所有摄取节点、所有仅投票节点、所有机器学习节点和所有协调节点添加到子集中。master:false,data:false,ingest:false,voting_only:true,ml:false或coordinating_only:false, 分别意味着将所有主节点、所有数据节点、所有摄取节点、所有仅投票节点、所有机器学习节点和所有协调节点排除在子集外。- 配对模式,使用
*通配符,格式为attrname:attrvalue,将所有具有自定义节点属性的节点添加到子集中,其名称和值与相应的模式匹配。自定义节点属性是通过node.attr.attrname: attrvalue形式在配置文件中设置的。
# 如果没有给出过滤器,默认是查询所有节点
GET /_nodes
# 查询所有节点
GET /_nodes/_all
# 查询本地节点
GET /_nodes/_local
# 查询主节点
GET /_nodes/_master
# 根据名称查询节点(支持通配符)
GET /_nodes/node_name_goes_here
GET /_nodes/node_name_goes_*
# 根据地址查询节点(支持通配符)
GET /_nodes/10.0.0.3,10.0.0.4
GET /_nodes/10.0.0.*
# 根据规则查询节点
GET /_nodes/_all,master:false
GET /_nodes/data:true,ingest:true
GET /_nodes/coordinating_only:true
GET /_nodes/master:true,voting_only:false
# 根据自定义属性查询节点(如:查询配置文件中含 node.attr.rack:2 属性的节点)
GET /_nodes/rack:2
GET /_nodes/ra*:2
GET /_nodes/ra*:2*
集群健康 API
GET /_cluster/health
GET /_cluster/health?level=shards
GET /_cluster/health/kibana_sample_data_ecommerce,kibana_sample_data_flights
GET /_cluster/health/kibana_sample_data_flights?level=shards
集群状态 API
集群状态 API 返回表示整个集群状态的元数据。
GET /_cluster/state
节点 API
Elasticsearch 官方之 cat Nodes API——返回有关集群节点的信息。
# 查看默认的字段
GET /_cat/nodes?v=true
# 查看指定的字段
GET /_cat/nodes?v=true&h=id,ip,port,v,m
分片 API
Elasticsearch 官方之 cat Shards API——shards 命令是哪些节点包含哪些分片的详细视图。它会告诉你它是主还是副本、文档数量、它在磁盘上占用的字节数以及它所在的节点。
# 查看默认的字段
GET /_cat/shards
# 根据名称查询分片(支持通配符)
GET /_cat/shards/my-index-*
# 查看指定的字段
GET /_cat/shards?h=index,shard,prirep,state,unassigned.reason
监控 API
Elasticsearch 中集群相关的健康、统计等相关的信息都是围绕着 cat API 进行的。
通过 GET 请求发送 cat,下面列出了所有可用的 API:
GET /_cat
=^.^=
/_cat/allocation
/_cat/shards
/_cat/shards/{index}
/_cat/master
/_cat/nodes
/_cat/tasks
/_cat/indices
/_cat/indices/{index}
/_cat/segments
/_cat/segments/{index}
/_cat/count
/_cat/count/{index}
/_cat/recovery
/_cat/recovery/{index}
/_cat/health
/_cat/pending_tasks
/_cat/aliases
/_cat/aliases/{alias}
/_cat/thread_pool
/_cat/thread_pool/{thread_pools}
/_cat/plugins
/_cat/fielddata
/_cat/fielddata/{fields}
/_cat/nodeattrs
/_cat/repositories
/_cat/snapshots/{repository}
/_cat/templates