ElasticSearch Rest API
Elasticsearch 是一个分布式、RESTful 风格的搜索和数据分析引擎
Elasticsearch 基于搜索库 Lucene 开发。ElasticSearch 隐藏了 Lucene 的复杂性,提供了简单易用的 REST API / Java API 接口(另外还有其他语言的 API 接口)。
_以下简称 ES_。
REST API 最详尽的文档应该参考:ES 官方 REST API
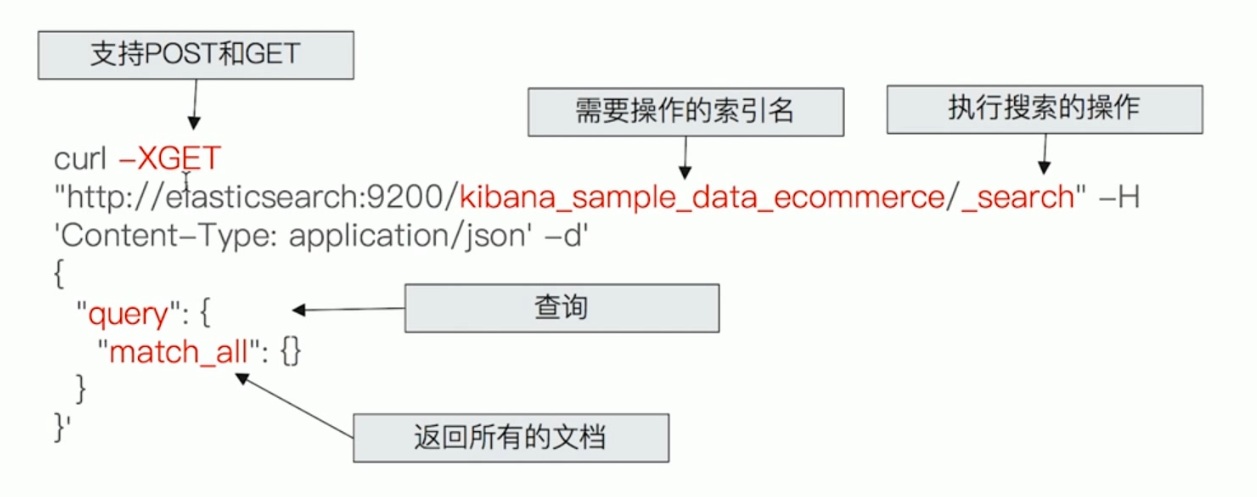
ElasticSearch Rest API 语法格式 向 Elasticsearch 发出的请求的组成部分与其它普通的 HTTP 请求是一样的:
1 curl -X<VERB> '<PROTOCOL>://<HOST>:<PORT>/<PATH>?<QUERY_STRING>' -d '<BODY>'
VERB:HTTP 方法,支持:GET, POST, PUT, HEAD, DELETEPROTOCOL:http 或者 https 协议(只有在 Elasticsearch 前面有 https 代理的时候可用)HOST:Elasticsearch 集群中的任何一个节点的主机名,如果是在本地的节点,那么就叫 localhostPORT:Elasticsearch HTTP 服务所在的端口,默认为 9200 PATH API 路径(例如_count 将返回集群中文档的数量),PATH:可以包含多个组件,例如 _cluster/stats 或者 _nodes/stats/jvmQUERY_STRING:一些可选的查询请求参数,例如?pretty 参数将使请求返回更加美观易读的 JSON 数据BODY:一个 JSON 格式的请求主体(如果请求需要的话)
ElasticSearch Rest API 分为两种:
URI Search :在 URL 中使用查询参数Request Body Search :基于 JSON 格式的、更加完备的 DSL
URI Search 示例:
Request Body Search 示例:
索引 API
参考资料:Elasticsearch 官方之 cat 索引 API
创建索引 新建 Index,可以直接向 ES 服务器发出 PUT 请求。
语法格式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 PUT /my_index { "settings" : { ... any settings ... }, "mappings" : { "type_one" : { ... any mappings ... }, "type_two" : { ... any mappings ... }, ... } }
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 PUT /user { "settings" : { "index" : { "number_of_shards" : 3, "number_of_replicas" : 2 } } }
服务器返回一个 JSON 对象,里面的 acknowledged 字段表示操作成功。
1 {"acknowledged" :true ,"shards_acknowledged" :true ,"index" :"user" }
如果你想禁止自动创建索引,可以通过在 config/elasticsearch.yml 的每个节点下添加下面的配置:
1 action.auto_create_index : false
删除索引 然后,我们可以通过发送 DELETE 请求,删除这个 Index。
删除多个索引
1 2 DELETE /index_one,index_twoDELETE /index_*
查看索引 可以通过 GET 请求查看索引信息
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_count GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search GET /_cat/indices/kibana*?v&s=index GET /_cat/indices?v&health=green GET /_cat/indices?v&s=docs.count:desc GET /_cat/indices/kibana*?pri&v&h=health,index,pri,rep,docs.count,mt GET /_cat/indices?v&h=i,tm&s=tm:desc
索引别名 ES 的索引别名就是给一个索引或者多个索引起的另一个名字,典型的应用场景是针对索引使用的平滑切换。
首先,创建索引 my_index,然后将别名 my_alias 指向它,示例如下:
1 2 PUT /my_index PUT /my_index/_alias/my_alias
也可以通过如下形式:
1 2 3 4 5 6 POST /_aliases { "actions" : [ { "add" : { "index" : "my_index" , "alias" : "my_alias" }} ] }
也可以在一次请求中增加别名和移除别名混合使用:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 POST /_aliases { "actions" : [ { "remove" : { "index" : "my_index" , "alias" : "my_alias" }} { "add" : { "index" : "my_index_v2" , "alias" : "my_alias" }} ] }
需要注意的是,如果别名与索引是一对一的,使用别名索引文档或者查询文档是可以的,但是如果别名和索引是一对多的,使用别名会发生错误,因为 ES 不知道把文档写入哪个索引中去或者从哪个索引中读取文档。
ES 索引别名有个典型的应用场景是平滑切换,更多细节可以查看 Elasticsearch(ES)索引零停机(无需重启)无缝平滑切换的方法 。
打开/关闭索引 通过在 POST 中添加 _close 或 _open 可以打开、关闭索引。
打开索引
1 2 3 4 POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_open POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_close
文档 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 POST users /_doc { "user" : "Mike" , "post_date" : "2019-04-15T14:12:12" , "message" : "trying out Kibana" } PUT users /_doc/1?op_type=create { "user" : "Jack" , "post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12" , "message" : "trying out Elasticsearch" } PUT users /_create/1 { "user" : "Jack" , "post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12" , "message" : "trying out Elasticsearch" } GET users /_doc/1 GET users /_doc/1 PUT users /_doc/1 { "user" : "Mike" } POST users /_update/1/ { "doc" :{ "post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12" , "message" : "trying out Elasticsearch" } } DELETE users /_doc/1 POST _bulk { "index" : { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "1" } } { "field1" : "value1" } { "delete" : { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "2" } } { "create" : { "_index" : "test2" , "_id" : "3" } } { "field1" : "value3" } { "update" : {"_id" : "1" , "_index" : "test" } } { "doc" : {"field2" : "value2" } } POST _bulk { "index" : { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "1" } } { "field1" : "value1" } { "delete" : { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "2" } } { "create" : { "_index" : "test2" , "_id" : "3" } } { "field1" : "value3" } { "update" : {"_id" : "1" , "_index" : "test" } } { "doc" : {"field2" : "value2" } } GET /_mget { "docs" : [ { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "1" }, { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "2" } ] } GET /test/_mget { "docs" : [ { "_id" : "1" }, { "_id" : "2" } ] } GET /_mget { "docs" : [ { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "1" , "_source" : false }, { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "2" , "_source" : ["field3" , "field4" ] }, { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "3" , "_source" : { "include" : ["user" ], "exclude" : ["user.location" ] } } ] } POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_msearch {} {"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size" :1} {"index" : "kibana_sample_data_flights" } {"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size" :2} DELETE users DELETE test DELETE test2
创建文档 指定 ID 语法格式:
1 PUT /_index/_type/_create/_id
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 PUT /user/_doc/_create/1 { "user" : "张三" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "数据库管理" }
注意:指定 Id,如果 id 已经存在,则报错
自动生成 ID 新增记录的时候,也可以不指定 Id,这时要改成 POST 请求。
语法格式:
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 POST /user/_doc { "user" : "张三" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "超级管理员" }
删除文档 语法格式:
示例:
更新文档 先删除,再写入 语法格式:
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 PUT /user/_doc/1 { "user" : "李四" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "超级管理员" }
在原文档上增加字段 语法格式:
1 POST /_index/_update/_id
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 POST /user/_update/1 { "doc" :{ "age" : "30" } }
查询文档 指定 ID 查询 语法格式:
示例:
结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 { "_index" : "user" , "_type" : "_doc" , "_id" : "1" , "_version" : 1 , "_seq_no" : 536248 , "_primary_term" : 2 , "found" : true , "_source" : { "user" : "张三" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "数据库管理" } }
返回的数据中,found 字段表示查询成功,_source 字段返回原始记录。
如果 id 不正确,就查不到数据,found 字段就是 false
查询所有记录 使用 GET 方法,直接请求 /index/type/_search,就会返回所有记录。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 $ curl 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search?pretty' { "took" : 1, "timed_out" : false , "_shards" : { "total" : 3, "successful" : 3, "skipped" : 0, "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : 2, "max_score" : 1.0, "hits" : [ { "_index" : "user" , "_type" : "admin" , "_id" : "WWuoDG8BHwECs7SiYn93" , "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "user" : "李四" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "系统管理" } }, { "_index" : "user" , "_type" : "admin" , "_id" : "1" , "_score" : 1.0, "_source" : { "user" : "张三" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "超级管理员" } } ] } }
上面代码中,返回结果的 took字段表示该操作的耗时(单位为毫秒),timed_out字段表示是否超时,hits字段表示命中的记录,里面子字段的含义如下。
total:返回记录数,本例是 2 条。max_score:最高的匹配程度,本例是1.0。hits:返回的记录组成的数组。
返回的记录中,每条记录都有一个_score字段,表示匹配的程序,默认是按照这个字段降序排列。
全文搜索 ES 的查询非常特别,使用自己的查询语法 ,要求 GET 请求带有数据体。
1 2 3 4 $ curl -H 'Content-Type: application/json' 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "管理" }} }'
上面代码使用 Match 查询 ,指定的匹配条件是desc字段里面包含”软件”这个词。返回结果如下。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 { "took" : 2 , "timed_out" : false , "_shards" : { "total" : 3 , "successful" : 3 , "skipped" : 0 , "failed" : 0 }, "hits" : { "total" : 2 , "max_score" : 0.38200712 , "hits" : [ { "_index" : "user" , "_type" : "admin" , "_id" : "WWuoDG8BHwECs7SiYn93" , "_score" : 0.38200712 , "_source" : { "user" : "李四" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "系统管理" } }, { "_index" : "user" , "_type" : "admin" , "_id" : "1" , "_score" : 0.3487891 , "_source" : { "user" : "张三" , "title" : "工程师" , "desc" : "超级管理员" } } ] } }
Elastic 默认一次返回 10 条结果,可以通过size字段改变这个设置,还可以通过from字段,指定位移。
1 2 3 4 5 6 $ curl 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search' -d ' { "query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "管理" }}, "from": 1, "size": 1 }'
上面代码指定,从位置 1 开始(默认是从位置 0 开始),只返回一条结果。
逻辑运算 如果有多个搜索关键字, Elastic 认为它们是or关系。
1 2 3 4 $ curl 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search' -d ' { "query" : { "match" : { "desc" : "软件 系统" }} }'
上面代码搜索的是软件 or 系统。
如果要执行多个关键词的and搜索,必须使用布尔查询 。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 $ curl -H 'Content-Type: application/json' 'localhost:9200/user/admin/_search?pretty' -d ' { "query": { "bool": { "must": [ { "match": { "desc": "管理" } }, { "match": { "desc": "超级" } } ] } } }'
批量执行 支持在一次 API 调用中,对不同的索引进行操作
支持四种类型操作
index
create
update
delete
操作中单条操作失败,并不会影响其他操作。
返回结果包括了每一条操作执行的结果。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 POST _bulk { "index" : { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "1" } } { "field1" : "value1" } { "delete" : { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "2" } } { "create" : { "_index" : "test2" , "_id" : "3" } } { "field1" : "value3" } { "update" : {"_id" : "1" , "_index" : "test" } } { "doc" : {"field2" : "value2" } }
说明:上面的示例如果执行多次,执行结果都不一样。
批量读取 读多个索引
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 GET /_mget { "docs" : [ { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "1" }, { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "2" } ] }
读一个索引
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 GET /test/_mget { "docs" : [ { "_id" : "1" }, { "_id" : "2" } ] } GET /_mget { "docs" : [ { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "1" , "_source" : false }, { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "2" , "_source" : ["field3" , "field4" ] }, { "_index" : "test" , "_id" : "3" , "_source" : { "include" : ["user" ], "exclude" : ["user.location" ] } } ] }
批量查询 1 2 3 4 5 POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_msearch {} {"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size" :1} {"index" : "kibana_sample_data_flights" } {"query" : {"match_all" : {}},"size" :2}
URI Search 查询语义 Elasticsearch URI Search 遵循 QueryString 查询语义,其形式如下:
1 2 3 4 GET /movies/_search?q=2012&df =title&sort =year:desc&from=0&size=10&timeout =1s { "profile" : true }
qdfsortprofile
1 2 3 4 GET /movies/_search?q=title:2012&sort =year:desc&from=0&size=10&timeout =1s { "profile" :"true" }
Term 和 Phrase Beautiful Mind 等效于 Beautiful OR Mind
“Beautiful Mind” 等效于 Beautiful AND Mind
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 GET /movies/_search?q=title:Beautiful Mind { "profile" :"true" } GET /movies/_search?q=title:"Beautiful Mind" { "profile" :"true" }
分组与引号 title:(Beautiful AND Mind)
title=”Beautiful Mind”
AND、OR、NOT 或者 &&、||、!
注意:AND、OR、NOT 必须大写
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful AND Mind) { "profile" :"true" } GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful NOT Mind) { "profile" :"true" }
范围查询
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautiful AND year:{2010 TO 2018%7D { "profile" :"true" } GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautiful AND year:[* TO 2018] { "profile" :"true" }
算数符号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 GET /movies/_search?q=year:>2010 { "profile" :"true" } GET /movies/_search?q=year:(>2010 && <=2018) { "profile" :"true" } GET /movies/_search?q=year:(+>2010 +<=2018) { "profile" :"true" }
通配符查询
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 GET /movies/_search?q=title:mi?d { "profile" :"true" } GET /movies/_search?q=title:b* { "profile" :"true" }
正则表达式 title:[bt]oy
模糊匹配与近似查询 示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautifl~1 { "profile" :"true" } GET /movies/_search?q=title:"Lord Rings" ~2 { "profile" :"true" }
Request Body & DSL Elasticsearch 除了 URI Search 查询方式,还支持将查询语句通过 Http Request Body 发起查询。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true { "profile" :"true" , "query" : { "match_all" : {} } }
分页 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true { "profile" : "true" , "from" : 0, "size" : 10, "query" : { "match_all" : {} } }
排序 最好在数字型或日期型字段上排序
因为对于多值类型或分析过的字段排序,系统会选一个值,无法得知该值
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true { "profile" : "true" , "sort" : [ { "order_date" : "desc" } ], "from" : 1, "size" : 10, "query" : { "match_all" : {} } }
_source 过滤 如果 _source 没有存储,那就只返回匹配的文档的元数据
_source 支持使用通配符,如:_source["name*", "desc*"]
示例:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true { "profile" : "true" , "_source" : [ "order_date" , "category.keyword" ], "from" : 1, "size" : 10, "query" : { "match_all" : {} } }
脚本字段 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 GET /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?ignore_unavailable=true { "profile" : "true" , "script_fields" : { "new_field" : { "script" : { "lang" : "painless" , "source" :"doc['order_date'].value+' hello'" } } }, "from" : 1, "size" : 10, "query" : { "match_all" : {} } }
使用查询表达式 - Match 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 POST movies/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "title" : "last christmas" } } } POST movies/_search { "query" : { "match" : { "title" : { "query" : "last christmas" , "operator" : "and" } } } }
短语搜索 - Match Phrase 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 POST movies/_search { "query" : { "match_phrase" : { "title" :{ "query" : "last christmas" } } } }
集群 API
Elasticsearch 官方之 Cluster API
一些集群级别的 API 可能会在节点的子集上运行,这些节点可以用节点过滤器指定。例如,任务管理、节点统计和节点信息 API 都可以报告来自一组过滤节点而不是所有节点的结果。
节点过滤器以逗号分隔的单个过滤器列表的形式编写,每个过滤器从所选子集中添加或删除节点。每个过滤器可以是以下之一:
_all:将所有节点添加到子集_local:将本地节点添加到子集_master:将当前主节点添加到子集根据节点 ID 或节点名将匹配节点添加到子集
根据 IP 地址或主机名将匹配节点添加到子集
使用通配符,将节点名、地址名或主机名匹配的节点添加到子集
master:true, data:true, ingest:true, voting_only:true, ml:true 或 coordinating_only:true, 分别意味着将所有主节点、所有数据节点、所有摄取节点、所有仅投票节点、所有机器学习节点和所有协调节点添加到子集中。master:false, data:false, ingest:false, voting_only:true, ml:false 或 coordinating_only:false, 分别意味着将所有主节点、所有数据节点、所有摄取节点、所有仅投票节点、所有机器学习节点和所有协调节点排除在子集外。配对模式,使用 * 通配符,格式为 attrname:attrvalue,将所有具有自定义节点属性的节点添加到子集中,其名称和值与相应的模式匹配。自定义节点属性是通过 node.attr.attrname: attrvalue 形式在配置文件中设置的。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 GET /_nodes GET /_nodes/_all GET /_nodes/_local GET /_nodes/_master GET /_nodes/node_name_goes_here GET /_nodes/node_name_goes_* GET /_nodes/10.0.0.3,10.0.0.4 GET /_nodes/10.0.0.* GET /_nodes/_all,master:false GET /_nodes/data:true ,ingest:true GET /_nodes/coordinating_only:true GET /_nodes/master:true ,voting_only:false GET /_nodes/rack:2 GET /_nodes/ra*:2 GET /_nodes/ra*:2*
集群健康 API 1 2 3 4 GET /_cluster/health GET /_cluster/health?level=shards GET /_cluster/health/kibana_sample_data_ecommerce,kibana_sample_data_flights GET /_cluster/health/kibana_sample_data_flights?level=shards
集群状态 API 集群状态 API 返回表示整个集群状态的元数据。
节点 API
Elasticsearch 官方之 cat Nodes API ——返回有关集群节点的信息。
1 2 3 4 GET /_cat/nodes?v=true GET /_cat/nodes?v=true &h=id ,ip,port,v,m
分片 API
Elasticsearch 官方之 cat Shards API ——shards 命令是哪些节点包含哪些分片的详细视图。它会告诉你它是主还是副本、文档数量、它在磁盘上占用的字节数以及它所在的节点。
1 2 3 4 5 6 GET /_cat/shards GET /_cat/shards/my-index-* GET /_cat/shards?h=index,shard,prirep,state,unassigned.reason
监控 API Elasticsearch 中集群相关的健康、统计等相关的信息都是围绕着 cat API 进行的。
通过 GET 请求发送 cat,下面列出了所有可用的 API:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 GET /_cat =^.^= /_cat/allocation /_cat/shards /_cat/shards/{index} /_cat/master /_cat/nodes /_cat/tasks /_cat/indices /_cat/indices/{index} /_cat/segments /_cat/segments/{index} /_cat/count /_cat/count/{index} /_cat/recovery /_cat/recovery/{index} /_cat/health /_cat/pending_tasks /_cat/aliases /_cat/aliases/{alias } /_cat/thread_pool /_cat/thread_pool/{thread_pools} /_cat/plugins /_cat/fielddata /_cat/fielddata/{fields} /_cat/nodeattrs /_cat/repositories /_cat/snapshots/{repository} /_cat/templates
参考资料