《极客时间教程 - Elasticsearch 核心技术与实战》笔记一
《极客时间教程 - Elasticsearch 核心技术与实战》笔记一
第一章:概述
课程介绍(略)
课程综述及学习建议(略)
Elasticsearch 概述及其发展历史
Elasticsearch 是一款基于 Lucene 的开源分布式搜索引擎。
- 1.0(2014 年 1 月)
- 5.0(2016 年 10 月)
- Lucene 6.x
- 默认打分机制从 TD-IDF 改为 BM 25
- 支持 Keyword 类型
- 6.0(2017 年 10 月)
- Lucene 7.x
- 跨集群复制
- 索引生命周期管理
- SQL 的支持
- 7.0(2019 年 4 月)
- Lucene 7.x
- 移除 Type
- ECK (用于支持 K8S)
- 集群协调
- High Level Rest Client
- Script Score 查询
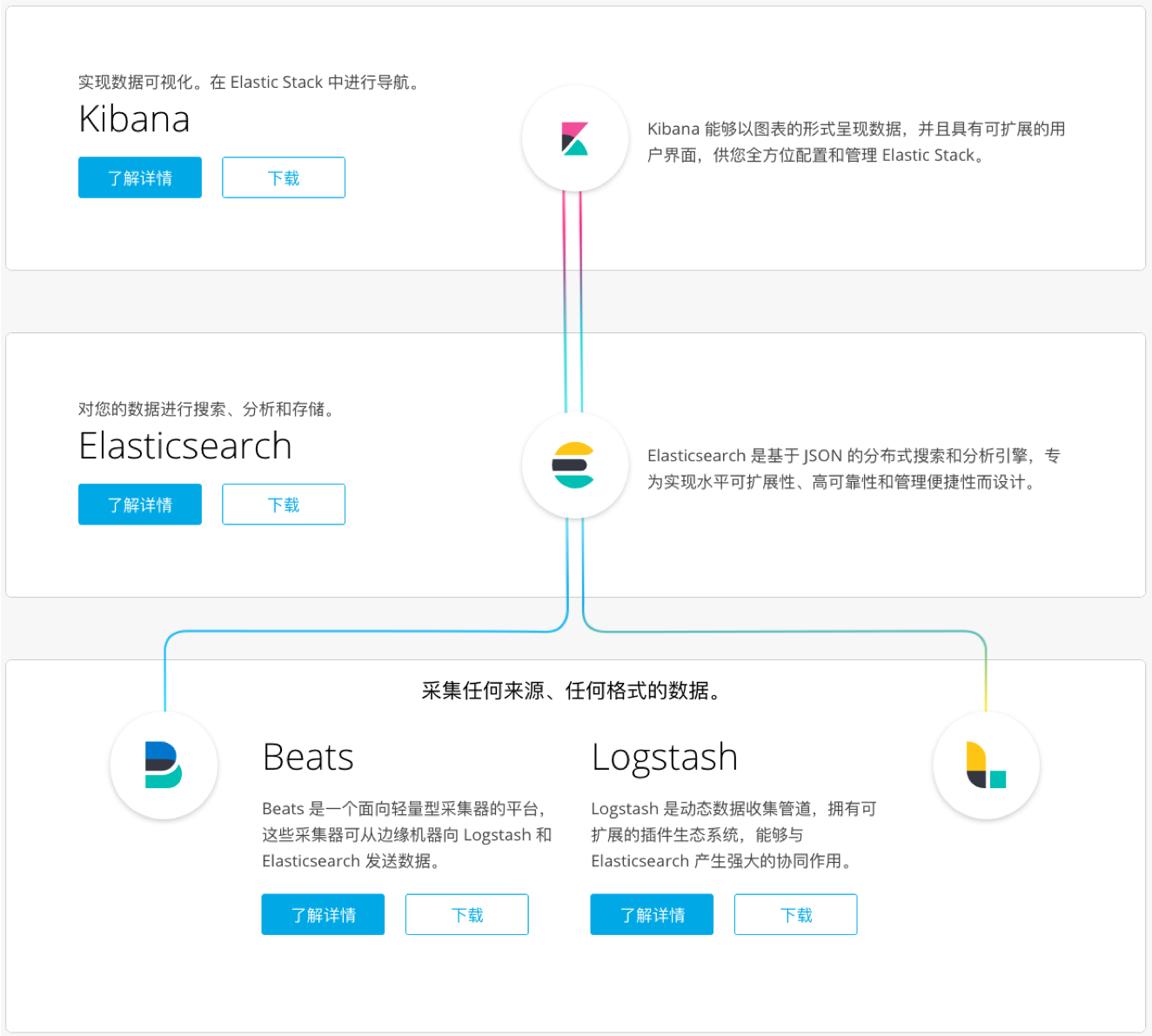
Elastic Stack 家族成员及其应用场景
Elasticsearch、Logstash、Kibana
Beats - 各种采集器
X-Pack - 商业化套件
第二章:安装上手
Elasticsearch 的安装与简单配置
【示例】
#启动单节点
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node0 -E cluster.name=geektime -E path.data=node0_data
#安装插件
bin/elasticsearch-plugin install analysis-icu
#查看插件
bin/elasticsearch-plugin list
#查看安装的插件
GET http://localhost:9200/_cat/plugins?v
#start multi-nodes Cluster
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node0 -E cluster.name=geektime -E path.data=node0_data
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node1 -E cluster.name=geektime -E path.data=node1_data
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node2 -E cluster.name=geektime -E path.data=node2_data
bin/elasticsearch -E node.name=node3 -E cluster.name=geektime -E path.data=node3_data
#查看集群
GET http://localhost:9200
#查看 nodes
GET _cat/nodes
GET _cluster/health
Kibana 的安装与界面快速浏览
#启动 kibana
bin/kibana
#查看插件
bin/kibana-plugin list
资料:
在 Docker 容器中运行 Elasticsearch,Kibana 和 Cerebro
Logstash 安装与导入数据
Elasticsearch 入门
基本概念 1 索引文档和 RESTAPI
基本概念:
- Document
- Elasticsearch 是面向文档的,文档是所有可搜索数据的最小单位。
- Elasticsearch 中,文档会被序列化成 JSON 格式保存。无模式。
- 每个文档都有一个唯一性 ID,如果没有指定,ES 会自动生成。
- Field - 文档包含一组字段。每个字段有对应类型(字符串、数值、布尔、日期、二进制、范围)
- 元数据(内置字段) - 以
_开头_index- 文档所属索引_type- 文档所属类型_id- 文档的唯一 ID_source- 文档的原始数据(JSON)_all- 整合所有字段内容到该字段,已废弃_version- 文档版本_score- 相关性打分
- 元数据(内置字段) - 以
- Index - Document 的容器。
- Mapping - 定义文档字段类型
- Setting - 定义不同数据分布
- Type - 7.0 移除 Type,每个 Index 只有一个名为
_doc的 Type。 - Node
- Shard
- Cluster
【示例】
#查看索引相关信息
GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce
#查看索引的文档总数
GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_count
#查看前 10 条文档,了解文档格式
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
}
#_cat indices API
#查看 indices
GET /_cat/indices/kibana*?v&s=index
#查看状态为绿的索引
GET /_cat/indices?v&health=green
#按照文档个数排序
GET /_cat/indices?v&s=docs.count:desc
#查看具体的字段
GET /_cat/indices/kibana*?pri&v&h=health,index,pri,rep,docs.count,mt
#How much memory is used per index?
GET /_cat/indices?v&h=i,tm&s=tm:desc
基本概念 2 - 集群、节点、分片、副本
集群的作用:高可用、可扩展
ES 集群通过集群名来区分。集群名通过配置文件或 -E cluster.name=xxx 来指定。
ES 节点通过配置文件或 -E node.name=xxx 指定。
每个 ES 节点启动后,会分配一个 UID,保存在 data 目录下
master 候选节点和 master 节点
每个节点启动后,默认就是一个 master 候选节点。候选节点可以通过选举,成为 master 节点。
集群中第一个节点启动时,会将自己选举为 master 节点。
每个节点上都保存了集群的状态,只有 master 节点才能修改集群的状态信息(通过集中式管理,保证数据一致性)。
集群状态信息:
- 所有的节点信息
- 所有的索引和相关 mapping、setting 信息
- 分片的路由信息
data node 和 coordinating node
- data node - 保存数据的节点,叫做 data node。负责保存分片数据。
- coordinating node - 负责接受 client 请求,将请求分发到合适节点,最终把结果汇聚到一起。每个节点默认都有 coordinating node 的职责。
其他节点类型
hot & warm 节点 - 不同硬件配置的 data node,用来实现 hot & warm 架构,降低集群部署成本。
机器学习节点 - 负责跑机器学习的 Job,用来做异常检测
tribe 节点 - 连接到不同的 ES 集群
分片
主分片 - 用于水平扩展,以提升系统可承载的总数据量以及吞吐量。
- 一个分片是一个运行 Lucene 实例
- 主分片数在索引创建时指定,后续不允许修改,除非 reindex
副分片(副本) - 用于冗余,解决高可用的问题。
- 副本数,可以动态调整
- 增加副本数,可以在一定程度上提高服务的可用性,以及查询的吞吐量。
生产环境的分片数,需要提前规划:
分片数过小:
- 无法通过增加节点实现水平扩展
- 单个分片的数据量太大,导致数据重新分配耗时
分片数过大:
- 影响搜索结果的相关性打分,影响统计结果的准确性
- 单个节点上过多的分片,会导致资源浪费,同时也会影响性能
- 7.0 开始,默认主分片数设置为 1, 解决了 over-sharding 的问题
查看集群健康状态
GET _cluster/health 有三种结果:
- Green - 主分片和副本都正常分配
- Yellow - 主分片全部正常分配,有副本分片未能正常分配
- Red - 有主分片未能分配
【示例】
get _cat/nodes?v
GET /_nodes/es7_01,es7_02
GET /_cat/nodes?v
GET /_cat/nodes?v&h=id,ip,port,v,m
GET _cluster/health
GET _cluster/health?level=shards
GET /_cluster/health/kibana_sample_data_ecommerce,kibana_sample_data_flights
GET /_cluster/health/kibana_sample_data_flights?level=shards
#### cluster state
The cluster state API allows access to metadata representing the state of the whole cluster. This includes information such as
GET /_cluster/state
#cluster get settings
GET /_cluster/settings
GET /_cluster/settings?include_defaults=true
GET _cat/shards
GET _cat/shards?h=index,shard,prirep,state,unassigned.reason
文档的基本 CRUD 和批量操作
文档的 CRUD
- create - 创建文档,如果 ID 已存在,会失败
- update - 增量更新文档,且文档必须已存在
- index - 若文档不存在,则创建新文档;若文档存在,则删除现有文档,再创建新文档,同时 version+1
- delete - DELETE
<index>/_doc/1 - read
【示例】
# create document. 自动生成 _id
POST users/_doc
{
"user" : "Mike",
"post_date" : "2019-04-15T14:12:12",
"message" : "trying out Kibana"
}
#create document. 指定 Id。如果 id 已经存在,报错
PUT users/_doc/1?op_type=create
{
"user" : "Jack",
"post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12",
"message" : "trying out Elasticsearch"
}
#create document. 指定 ID 如果已经存在,就报错
PUT users/_create/1
{
"user" : "Jack",
"post_date" : "2019-05-15T14:12:12",
"message" : "trying out Elasticsearch"
}
### Get Document by ID
#Get the document by ID
GET users/_doc/1
### Index & Update
#Update 指定 ID (先删除,在写入)
GET users/_doc/1
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"user" : "Mike"
}
#GET users/_doc/1
#在原文档上增加字段
POST users/_update/1/
{
"doc": {
"post_date": "2019-05-15T14:12:12",
"message": "trying out Elasticsearch"
}
}
### Delete by Id
# 删除文档
DELETE users/_doc/1
批量写
bulk API 支持四种类型:
- index
- create
- update
- delete
### Bulk 操作
#执行两次,查看每次的结果
#执行第 1 次
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "field1" : "value1" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test2", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "field1" : "value3" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_index" : "test"} }
{ "doc" : {"field2" : "value2"} }
#执行第 2 次
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "1" } }
{ "field1" : "value1" }
{ "delete" : { "_index" : "test", "_id" : "2" } }
{ "create" : { "_index" : "test2", "_id" : "3" } }
{ "field1" : "value3" }
{ "update" : {"_id" : "1", "_index" : "test"} }
{ "doc" : {"field2" : "value2"} }
批量读
mget
msearch
### mget 操作
GET /_mget
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1"
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2"
}
]
}
#URI 中指定 index
GET /test/_mget
{
"docs": [
{
"_id": "1"
},
{
"_id": "2"
}
]
}
GET /_mget
{
"docs": [
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "1",
"_source": false
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "2",
"_source": [
"field3",
"field4"
]
},
{
"_index": "test",
"_id": "3",
"_source": {
"include": [
"user"
],
"exclude": [
"user.location"
]
}
}
]
}
### msearch 操作
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_msearch
{}
{"query":{"match_all":{}},"size":1}
{"index":"kibana_sample_data_flights"}
{"query":{"match_all":{}},"size":2}
### 清除测试数据
#清除数据
DELETE users
DELETE test
DELETE test2
倒排索引入门
什么是正排,什么是倒排?
- ** 正排 **:文档 ID 到文档内容和单词的关联
- ** 倒排 **:单词到文档 ID 的关系
倒排索引含两个部分
- ** 单词词典 ** - 记录所有文档的单词,记录单词到倒排列表的关联关系
- ** 倒排列表 ** - 记录了单词对应的文档结合,由倒排索引项组成。
倒排索引项:
- 文档 ID
- 词频 TF - 单词在文档中出现的次数,用于相关性评分
- 位置 - 单词文档中分词的位置。用于语句搜索
- 偏移 - 记录单词的开始结束位置,实现高亮显示
要点:
- 文档中每个字段都有自己的倒排索引
- 可以指定某些字段不做索引
【示例】
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "Mastering Elasticsearch"
}
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "Elasticsearch Server"
}
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "Elasticsearch Essentials"
}
通过分析器进行分词
** 分词 **:文本分析是把全文本转换一系列单词(term / token)的过程。
分析组件由如下三部分组成,它的执行顺序如下:
Character Filters -> Tokenizer -> Token Filters
说明:
- Character Filters(字符过滤器) - 针对原始文本处理, 例如去除特殊字符、过了 html 标签
- Tokenizer(分词器) - 按照策略将文本切分为单词
- Token Filters(分词过滤器) - 对切分的单词进行加工,如:转为小写、删除 stop word、增加同义词等
ES 内置分析器:
- Standard Analyzer - 默认分词器,按词切分,小写处理。
- Simple Analyzer - 按非字母切分(过滤符号),小写处理。
- Whitespace Analyzer - 按空格切分,不转小写。
- Stop Analyzer - 小写处理,停用词过滤。
- Keyword Analyzer - 不分词,直接将输入当做输出。
- Pattern Analyzer - 按正则分词,默认正则为
\W+。 - Language Analyzers - 提供 30 多种常见语言的分词器。
- Fingerprint Analyzer - 可用于重复检测的指纹。
中文分词
elasticsearch-analysis-ik
elasticsearch-thulac-plugin
【示例】
#查看不同的 analyzer 的效果
#standard
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "2 running Quick brown-foxes leap over lazy dogs in the summer evening."
}
#simpe
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "simple",
"text": "2 running Quick brown-foxes leap over lazy dogs in the summer evening."
}
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "stop",
"text": "2 running Quick brown-foxes leap over lazy dogs in the summer evening."
}
#stop
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "whitespace",
"text": "2 running Quick brown-foxes leap over lazy dogs in the summer evening."
}
#keyword
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "keyword",
"text": "2 running Quick brown-foxes leap over lazy dogs in the summer evening."
}
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "pattern",
"text": "2 running Quick brown-foxes leap over lazy dogs in the summer evening."
}
#english
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "english",
"text": "2 running Quick brown-foxes leap over lazy dogs in the summer evening."
}
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "icu_analyzer",
"text": "他说的确实在理”"
}
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "他说的确实在理”"
}
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "icu_analyzer",
"text": "这个苹果不大好吃"
}
SearchAPI 概览
ES Search 有两种类型:
- URI 查询 - 在 URL 中使用查询
- Request Body 查询 - 基于 JSON 格式的 DSL
| 语法 | 范围 |
|---|---|
/_search | 集群上的所有索引 |
/index1/_search | index1 |
/index1,index2/_search | index1 和 index2 |
/index*/_search | 以 index 开头的索引 |
【示例】
#URI Query
GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search?q=customer_first_name:Eddie
GET kibana*/_search?q=customer_first_name:Eddie
GET /_all/_search?q=customer_first_name:Eddie
#REQUEST Body
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
"profile": true,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
URISearch 详解
使用 q 指定查询字符串(query string)
q- 指定查询语句,使用 Query String 语义df- 默认字段sort- 排序from/size- 分页profile- 显示查询是如何被执行的
指定字段 vs. 泛查询
- q=title:2012 / q=2012
Term vs. Phrase
- Beautiful Mind,等效于 Beautiful Or Mind
- "Beautiful Mind",等效于 Beautiful And Mind
分组与引号
- title:(Beautiful And Mind)
- title="Beautiful Mind"
布尔操作
- AND / OR / NOT 或
&&/||/! - 必须大写
title:(matrix NOT reloaded)
分组
+表示 must-表示 must_nottitle:(+matrix -reloaded)
范围查询
区间表示:[] 闭区间,{} 开区间
year:{2019 TO 2018}year:{* TO 2018}
算数符号
year:>2010year:(>2010 && <=2018)year:(+>2010 +<=2018)
通配符查询(通配符查询效率低,占用内存大,不建议使用。特别是放在最前面)
? 表示 1 个字符;* 表示任意个字符
title:mi?dtitle:be*
正则表达式
title:[bt]oy
模糊匹配与近似查询
title:befutifl~1title:"lord rings"~2
#基本查询
GET /movies/_search?q=2012&df=title&sort=year:desc&from=0&size=10&timeout=1s
#带 profile
GET /movies/_search?q=2012&df=title
{
"profile":"true"
}
#泛查询,正对 _all, 所有字段
GET /movies/_search?q=2012
{
"profile":"true"
}
#指定字段
GET /movies/_search?q=title:2012&sort=year:desc&from=0&size=10&timeout=1s
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 查找美丽心灵,Mind 为泛查询
GET /movies/_search?q=title:Beautiful Mind
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 泛查询
GET /movies/_search?q=title:2012
{
"profile":"true"
}
#使用引号,Phrase 查询
GET /movies/_search?q=title:"Beautiful Mind"
{
"profile":"true"
}
#分组,Bool 查询
GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful Mind)
{
"profile":"true"
}
#布尔操作符
# 查找美丽心灵
GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful AND Mind)
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 查找美丽心灵
GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful NOT Mind)
{
"profile":"true"
}
# 查找美丽心灵
GET /movies/_search?q=title:(Beautiful %2BMind)
{
"profile":"true"
}
#范围查询 , 区间写法
GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautiful AND year:[2002 TO 2018%7D
{
"profile":"true"
}
#通配符查询
GET /movies/_search?q=title:b*
{
"profile":"true"
}
// 模糊匹配 & 近似度匹配
GET /movies/_search?q=title:beautifl~1
{
"profile":"true"
}
GET /movies/_search?q=title:"Lord Rings"~2
{
"profile":"true"
}
RequestBody 与 QueryDSL 简介
- DSL
- from / size(分页)
- sort(排序)
- _source(原文本查询)
- script_fields(脚本)
- match
- match_phrase
- simple_query_string
curl -XGET "http://localhost:9200/kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}'
#ignore_unavailable=true,可以忽略尝试访问不存在的索引“404_idx”导致的报错
#查询 movies 分页
POST /movies,404_idx/_search?ignore_unavailable=true
{
"profile": true,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
POST /kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
"from":10,
"size":20,
"query":{
"match_all": {}
}
}
#对日期排序
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
"sort":[{"order_date":"desc"}],
"query":{
"match_all": {}
}
}
#source filtering
POST kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
"_source":["order_date"],
"query":{
"match_all": {}
}
}
#脚本字段
GET kibana_sample_data_ecommerce/_search
{
"script_fields": {
"new_field": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "doc['order_date'].value+'hello'"
}
}
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
POST movies/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "last christmas"
}
}
}
POST movies/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "last christmas",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
POST movies/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title":{
"query": "one love"
}
}
}
}
POST movies/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title":{
"query": "one love",
"slop": 1
}
}
}
}
QueryString&SimpleQueryString 查询
PUT /users/_doc/1
{
"name":"Ruan Yiming",
"about":"java, golang, node, swift, elasticsearch"
}
PUT /users/_doc/2
{
"name":"Li Yiming",
"about":"Hadoop"
}
POST users/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"default_field": "name",
"query": "Ruan AND Yiming"
}
}
}
POST users/_search
{
"query": {
"query_string": {
"fields":["name","about"],
"query": "(Ruan AND Yiming) OR (Java AND Elasticsearch)"
}
}
}
#Simple Query 默认的 operator 是 Or
POST users/_search
{
"query": {
"simple_query_string": {
"query": "Ruan AND Yiming",
"fields": ["name"]
}
}
}
POST users/_search
{
"query": {
"simple_query_string": {
"query": "Ruan Yiming",
"fields": ["name"],
"default_operator": "AND"
}
}
}
GET /movies/_search
{
"profile": true,
"query":{
"query_string":{
"default_field": "title",
"query": "Beafiful AND Mind"
}
}
}
# 多 fields
GET /movies/_search
{
"profile": true,
"query":{
"query_string":{
"fields":[
"title",
"year"
],
"query": "2012"
}
}
}
GET /movies/_search
{
"profile":true,
"query":{
"simple_query_string":{
"query":"Beautiful +mind",
"fields":["title"]
}
}
}
DynamicMapping 和常见字段类型
什么是 Mapping
Mapping 类似数据库中 schema 的定义
Mapping 会将 JSON 文档映射成 Lucene 所需要的数据格式
一个 Mapping 属于一个索引的 Type
字段数据类型
- 简单类型
- Text / Keyword
- Date
- Integer / Floating
- Boolean
- Ipv4 / Ipv6
- 复杂类型
- 对象类型 / 嵌套类型
- 特殊类型
- get_point & geo_shape / percolator
什么是 Dynamic Mapping
在写入文档时,如果索引不存在,会自动创建索引
ES 会根据文档信息,自动推算出字段的类型
有时候,推算可能会不准确,当类型设置错误时,可能会导致一些功能无法正常运行。例如范围查询
能否更改 Mapping 的字段类型
Dynamic 设为 true 时,一旦有新增字段的文档写入,Mapping 也同时被更新
Dynamic 设为 false 时,Mapping 不会被更新,新增字段的数据无法被索引,但是信息会出现在 _source 中。
Dynamic 设为 stric 时,文档写入失败
对已有字段,一旦有数据写入,就不再支持修改字段的定义
如果希望改变字段类型,必须 reindex API,重建索引
【示例】
#写入文档,查看 Mapping
PUT mapping_test/_doc/1
{
"firstName":"Chan",
"lastName": "Jackie",
"loginDate":"2018-07-24T10:29:48.103Z"
}
#查看 Mapping 文件
GET mapping_test/_mapping
#Delete index
DELETE mapping_test
#dynamic mapping,推断字段的类型
PUT mapping_test/_doc/1
{
"uid" : "123",
"isVip" : false,
"isAdmin": "true",
"age":19,
"heigh":180
}
#查看 Dynamic
GET mapping_test/_mapping
#默认 Mapping 支持 dynamic,写入的文档中加入新的字段
PUT dynamic_mapping_test/_doc/1
{
"newField":"someValue"
}
#该字段可以被搜索,数据也在 _source 中出现
POST dynamic_mapping_test/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"newField":"someValue"
}
}
}
#修改为 dynamic false
PUT dynamic_mapping_test/_mapping
{
"dynamic": false
}
#新增 anotherField
PUT dynamic_mapping_test/_doc/10
{
"anotherField":"someValue"
}
#该字段不可以被搜索,因为 dynamic 已经被设置为 false
POST dynamic_mapping_test/_search
{
"query":{
"match":{
"anotherField":"someValue"
}
}
}
get dynamic_mapping_test/_doc/10
#修改为 strict
PUT dynamic_mapping_test/_mapping
{
"dynamic": "strict"
}
#写入数据出错,HTTP Code 400
PUT dynamic_mapping_test/_doc/12
{
"lastField":"value"
}
DELETE dynamic_mapping_test
显式 Mapping 设置与常见参数介绍
- index - 控制当前字段是否被索引
- index_options - 控制倒排索引记录的内容
- docs - 记录 doc id
- freqs - 记录 doc id 和 term freqencies
- positions - 记录 doc id 和 term freqencies、term position
- offsets - 记录 doc id 和 term freqencies、term position、char offsets
- null_value - 对 null 值实现搜索,只有 keyword 类型支持
- copy_to - _all 在 ES 7.X 被 copy_to 替代
ES 不提供专门的数组类型。但是任何字段 ,都可以包含多个相同类型的数值。
#设置 index 为 false
DELETE users
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"firstName": {
"type": "text"
},
"lastName": {
"type": "text"
},
"mobile": {
"type": "text",
"index": false
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"firstName":"Ruan",
"lastName": "Yiming",
"mobile": "12345678"
}
POST /users/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"mobile":"12345678"
}
}
}
#设定 Null_value
DELETE users
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"firstName": {
"type": "text"
},
"lastName": {
"type": "text"
},
"mobile": {
"type": "keyword",
"null_value": "NULL"
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"firstName":"Ruan",
"lastName": "Yiming",
"mobile": null
}
PUT users/_doc/2
{
"firstName": "Ruan2",
"lastName": "Yiming2"
}
GET users/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"mobile": "NULL"
}
}
}
#设置 Copy to
DELETE users
PUT users
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"firstName": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "fullName"
},
"lastName": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "fullName"
}
}
}
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"firstName": "Zhang",
"lastName": "Peng"
}
GET users/_search?q=fullName:(Zhang Peng)
POST users/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"fullName": {
"query": "Zhang Peng",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
#数组类型
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"name":"onebird",
"interests":"reading"
}
PUT users/_doc/1
{
"name":"twobirds",
"interests":["reading","music"]
}
POST users/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
GET users/_mapping
多字段特性及 Mapping 中配置自定义 Analyzer
ES 内置的分析器无法满足需求时,可以自定义分析器,通过组合不同组件来进行定制:
- Character Filter - html strip、mapping、pattern replace
- Tokenizer - whitespace、standard、uax_url_email、pattern、keyword、path hierarchy
- Token Filter - lowercase、stop、synonym
【示例】
PUT logs/_doc/1
{
"level": "DEBUG"
}
GET /logs/_mapping
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer":"keyword",
"char_filter":["html_strip"],
"text": "<b>hello world</b>"
}
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer":"path_hierarchy",
"text":"/user/ymruan/a/b/c/d/e"
}
#使用 char filter 进行替换
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": [
{
"type" : "mapping",
"mappings" : [ "- => _"]
}
],
"text": "123-456, I-test! test-990 650-555-1234"
}
# char filter 替换表情符号
POST _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": [
{
"type" : "mapping",
"mappings" : [ ":) => happy", ":( => sad"]
}
],
"text": ["I am felling :)", "Feeling :( today"]
}
# white space and snowball
GET _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": ["stop","snowball"],
"text": ["The gilrs in China are playing this game!"]
}
# whitespace 与 stop
GET _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": ["stop","snowball"],
"text": ["The rain in Spain falls mainly on the plain."]
}
# remove 加入 lowercase 后,The 被当成 stopword 删除
GET _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "whitespace",
"filter": ["lowercase","stop","snowball"],
"text": ["The gilrs in China are playing this game!"]
}
# 正则表达式
GET _analyze
{
"tokenizer": "standard",
"char_filter": [
{
"type": "pattern_replace",
"pattern": "http://(.*)",
"replacement": "$1"
}
],
"text": "http://www.elastic.co"
}
IndexTemplate 和 DynamicTemplate
集群上的索引会越来越多,可以根据时间周期性创建索引,例如:log-yyyyMMdd
index template - 帮助设定 mapping 和 setting,并按照一定规则,自动匹配到新创建的索引上。
- 模板仅在一个索引被新建时,才会起作用。修改模板不会影响已创建的索引。
- 可以设定多个索引模板,这些设置会被 merge 在一起
- 可以指定 order,以控制模板合并过程
什么是 Dynamic Template
根据 ES 识别的数据类型,结合字段名称,来动态设定字段类型
- 所有的字符串类型都设定成 keyword,或关闭 keyword 字段
- is 开头的字段都设置成 boolean
- long_ 开头的都设置成 long 类型
Dynamic Template 要点
- Dynamic Template 是定义在某索引的 mapping 中
- Template 有一个名称
- 匹配规则是一个数组
- 为匹配到字段设置 mapping
- match_mapping_type - 匹配自动识别的字段类型,如 string、boolean 等
- match、unmatch - 匹配字段名
- path_match、path_unmatch
【示例】
#数字字符串被映射成 text,日期字符串被映射成日期
PUT ttemplate/_doc/1
{
"someNumber":"1",
"someDate":"2019/01/01"
}
GET ttemplate/_mapping
#Create a default template
PUT _template/template_default
{
"index_patterns": ["*"],
"order" : 0,
"version": 1,
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas":1
}
}
PUT /_template/template_test
{
"index_patterns" : ["test*"],
"order" : 1,
"settings" : {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas" : 2
},
"mappings" : {
"date_detection": false,
"numeric_detection": true
}
}
#查看 template 信息
GET /_template/template_default
GET /_template/temp*
#写入新的数据,index 以 test 开头
PUT testtemplate/_doc/1
{
"someNumber":"1",
"someDate":"2019/01/01"
}
GET testtemplate/_mapping
get testtemplate/_settings
PUT testmy
{
"settings":{
"number_of_replicas":5
}
}
put testmy/_doc/1
{
"key":"value"
}
get testmy/_settings
DELETE testmy
DELETE /_template/template_default
DELETE /_template/template_test
#Dynaminc Mapping 根据类型和字段名
DELETE my_index
PUT my_index/_doc/1
{
"firstName":"Ruan",
"isVIP":"true"
}
GET my_index/_mapping
DELETE my_index
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"strings_as_boolean": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"match":"is*",
"mapping": {
"type": "boolean"
}
}
},
{
"strings_as_keywords": {
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}
]
}
}
DELETE my_index
#结合路径
PUT my_index
{
"mappings": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{
"full_name": {
"path_match": "name.*",
"path_unmatch": "*.middle",
"mapping": {
"type": "text",
"copy_to": "full_name"
}
}
}
]
}
}
PUT my_index/_doc/1
{
"name": {
"first": "John",
"middle": "Winston",
"last": "Lennon"
}
}
GET my_index/_search?q=full_name:John
Elasticsearch 聚合分析简介
聚合分类:
- Bucket - 一些字段满足特定条件的文档的集合(分组)
- Metric - 一些数学运算,可以对文档字段进行统计分析
- Pipeline - 对其他的聚合结果进行二次聚合
- Matrix - 支持对多个字段的操作并提供一个结果矩阵
聚合支持嵌套
【示例】
# 按照目的地进行分桶统计
GET kibana_sample_data_flights/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs":{
"flight_dest":{
"terms":{
"field":"DestCountry"
}
}
}
}
#查看航班目的地的统计信息,增加平均,最高最低价格
GET kibana_sample_data_flights/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs":{
"flight_dest":{
"terms":{
"field":"DestCountry"
},
"aggs":{
"avg_price":{
"avg":{
"field":"AvgTicketPrice"
}
},
"max_price":{
"max":{
"field":"AvgTicketPrice"
}
},
"min_price":{
"min":{
"field":"AvgTicketPrice"
}
}
}
}
}
}
#价格统计信息 + 天气信息
GET kibana_sample_data_flights/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"flight_dest": {
"terms": {
"field": "DestCountry"
},
"aggs": {
"stats_price": {
"stats": {
"field": "AvgTicketPrice"
}
},
"weather": {
"terms": {
"field": "DestWeather",
"size": 5
}
}
}
}
}
}